PMSM is a type of permanent magnet motor widely used in electric vehicles. The efficiency of the PMSM motor is 15% higher than that of the induction motor and it is the traction motor with the highest power density.
1. What is a PMSM Motor?
A permanent magnet synchronous motor is a type of AC synchronous motor whose magnetic field is excited by permanent magnets that produce a sinusoidal reverse electromagnetic field. It contains the same rotor and stator as an induction motor, but the rotor uses permanent magnets to produce the magnetic field. Therefore, there is no need to wind a field winding on the rotor. It is also called a three-phase brushless permanent magnet sine wave motor.
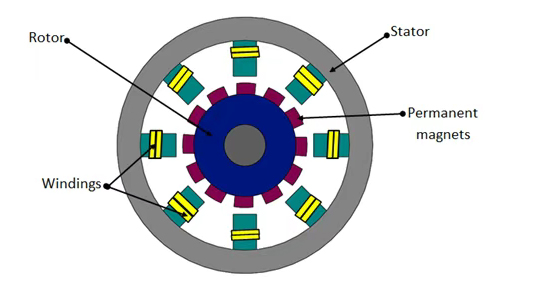
2. Principle of PMSM Motor
Compared with conventional motors, permanent magnet synchronous motors are highly efficient, brushless, fast, safe and highly dynamic. They produce smooth torque with low noise and are mainly used in high-speed applications such as robotics. It is a three-phase AC synchronous motor that operates synchronously with an applied AC power supply.
Instead of using windings, the rotor is equipped with permanent magnets to produce a rotating magnetic field. Since there is no DC power supply, this type of motor is straightforward and low-cost. It consists of a stator with 3 windings and a rotor with permanent magnets to produce magnetic field poles. It works by providing a three-phase input AC power supply to the stator.
The working principle of the PMSM motor is similar to that of the synchronous motor. It relies on a rotating magnetic field to generate an electromotive force at synchronous speed.
When the stator winding is energized by a three-phase power supply, a rotating magnetic field is generated between the air gaps. Torque is generated when the rotor poles maintain a rotating magnetic field at synchronous speed and the rotor rotates continuously. Since these motors are not self-starting motors, it is necessary to provide a variable frequency power supply.
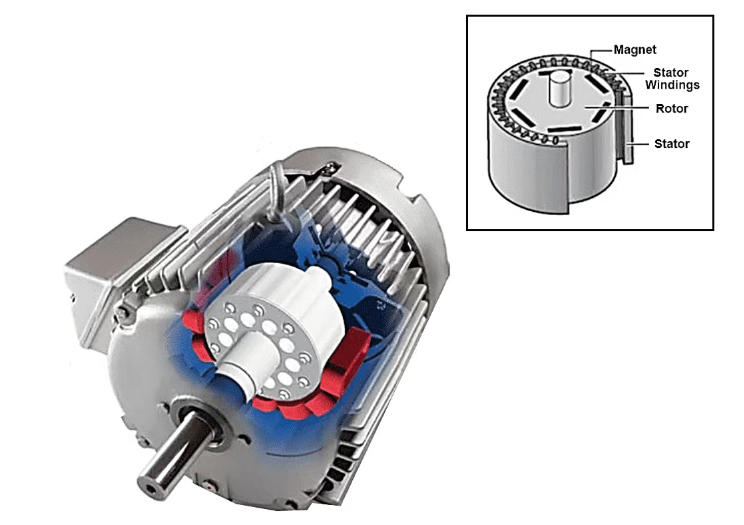
3. Structure of PMSM motor
The Stator of PMSM Motor:
As with normal AC induction motors, power is supplied through stator windings. PMSM stator windings are usually distributed over multiple slots to approximate a sinusoidal distribution, thus generating a sinusoidal back EMF waveform.
The Rotor of the PMSM Motor:
The structure of the PMSM motor is similar to the basic synchronous motor, the only difference is the rotor. The rotor has no field winding, but permanent magnets are used to generate field poles. The permanent magnets used in PMSM are composed of samarium cobalt and dielectric, iron and boron because of their high magnetic permeability.
The most widely used permanent magnet is neodymium boron iron because of its low cost and easy availability. In this type, the permanent magnets are mounted on the rotor. The structure of the permanent magnet synchronous motor can be divided into two types based on the way the permanent magnets are mounted on the rotor.
If the magnets are mounted on the surface of the motor rotor, the PMSM motor is called a surface-mounted permanent magnet (SPM).
If the magnets are mounted inside the rotor, the PMSM motor is called an interior permanent magnet (IPM). Motors with interior permanent magnet (IPM) rotors offer extremely high efficiency.
4. PMSM Motor Control Principle
The PMSM drive is a classic vector-controlled drive for permanent magnet synchronous motors. The drive uses closed-loop speed control based on a vector control method. The closed-loop configuration provides speed feedback. The feedback allows the drive to track the exact position of the rotor, providing a truly infinitely variable speed range, including full torque at zero speed.
PMSM motor require a position sensor on the rotor shaft. The most common sensors for motors are encoders and resolvers.
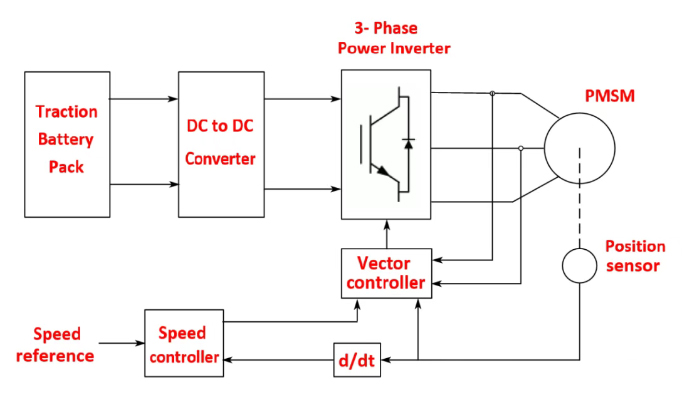
These permanent magnet drives use motor data and current measurements to calculate the rotor position; the calculations are quite accurate on a digital signal processor (DSP). At each sampling interval, the time- and speed-dependent three-phase AC system is converted to a rotating dual-coordinate system, where each current is expressed and controlled as the sum of two vectors.
Based on the vector control strategy, the stator current reference orthogonal and quadrature (dq) components corresponding to the commanded torque are derived. The reference dq components of the stator currents are then used to obtain the required gate drive signals for the inverter.
The main advantage of this drive is its fast dynamic response. The inherent coupling effect between torque and flux in the machine can be managed by decoupling control (stator flux orientation), which allows independent control of torque and flux. However, due to its computational complexity, the implementation of such a drive requires a fast computational processor or DSP.
5. Advantages and Disadvantages of PMSM Motors
Advantages:
PMSM motor has a strong overload capacity. The power density of PMSM is higher than that of induction motors.
Higher efficiency and smaller size than induction motors (PMSMs are only one-third the size of most AC motors, which makes installation and maintenance easier).
PMSM motor is able to maintain full torque at low speeds.
PMSM motors use magnets to generate the rotor magnetic field, rather than using the magnetizing component of the stator current as in induction motors. These magnets consume almost no power, so unlike AC induction motors and excited synchronous motors, the copper losses in the rotor are negligible.
PMSM motor has low rotor electrical losses and less heat dissipation than induction motors. In addition, since there is no mechanical collector and brushes to wear out like induction motors, there is less friction and high durability.
PMSM motor has low maintenance costs, high durability and reliability. For brushless and mechanical switches, the cost of regular maintenance is greatly reduced, and the risk of sparking in special environments is eliminated.
PMSM motor operate at a higher power factor, which improves the power factor of the entire system. Improved power factor also reduces system voltage drop and voltage drop at the motor terminals.
Provides smooth torque and dynamic performance.
Disadvantages:
These motors are very expensive compared to induction motors;
Since they are not self-starting motors, they are difficult to start;
We need a complex control system to control the stator current.
6. HONEST Automation: Electric Vehicle PMSM Motor Assembly Manufacturer
HONEST is a leading manufacturer of PMSM (Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor) assembly equipment for electric vehicles, specializing in providing innovative automation solutions for the electric vehicle and motor manufacturing industries. With years of industry experience and technical expertise, we offer highly efficient and precise PMSM motor assembly equipment to help our customers achieve higher production efficiency and product quality in the electric vehicle market. Our equipment is widely used in critical areas such as electric vehicle drive systems, ensuring motor performance stability and long lifespan.
HONEST tailors the most suitable equipment solutions for each customer based on a deep understanding of their needs and provides comprehensive technical support. No matter how complex your production requirements are, our expert team is ready to offer professional advice and customized solutions. If you would like to learn more about our technology or obtain a tailored solution, feel free to contact us anytime. HONEST is here to work with you and drive your business forward.






