An automatic transmission is a transmission device that can automatically shift gears according to the vehicle speed and engine speed relative to the manual transmission.
The main function of the transmission is to adjust the driving force and speed of the vehicle in real-time, in order to adapt to the actual road conditions faced by the vehicle in the process of use: for example, starting and stopping quickly, driving at low or high speeds, accelerating, decelerating, climbing and reversing, and so on. The core of the automatic transmission is to realize automatic shifting.
Automatic gear shifting means that when the car is driving, the driver controls the accelerator pedal according to the needs of the driving process, and the automatic transmission can automatically shift into different gears according to the engine load and the operating conditions of the vehicle.
A. Working Principle
The automatic transmission mainly realizes automatic shifting through the following core components:
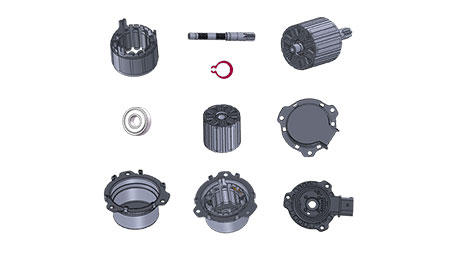
1. Torque Converter: The hydraulic torque converter is one of the core components of the hydraulic automatic transmission. It consists of a pump wheel, a turbine, and a guide wheel. The pump impeller is connected to the engine’s flywheel. When the engine is running, the pump impeller drives the transmission oil to flow. The transmission oil is accelerated by the blades of the pump wheel and then impacts the turbine, causing it to rotate and thereby transmit power to the input shaft of the transmission. The guide wheel is used to change the direction of the oil flow and further increase the turbine speed and torque.
2. Planetary Gear Transmission: The planetary gear transmission consists of multiple planetary rows, each of which consists of a sun gear, planetary gear, and ring gear. Through the combination and release of different clutches and brakes, different gear combinations can be formed to achieve different transmission ratios, thereby achieving automatic shifting.
3. Automatic Shift Control: The automatic transmission can automatically shift gears based on driving conditions. It is usually controlled by an electronic control unit (ECU) based on factors such as throttle position, vehicle speed, and engine load. The ECU will send signals to the hydraulic control unit, which then controls the work of the clutch and brake by adjusting the pressure and flow direction of the hydraulic oil to achieve automatic shifting.
4. Lockup Clutch: In a torque converter, there is usually a lockup clutch. When the vehicle speed reaches a certain level and the speed difference between the engine and the transmission is small, the lock-up clutch will engage, achieving a rigid connection between the pump wheel and the turbine, thus improving transmission efficiency and reducing energy loss.
B. Advantages
Easy Operation: The automatic transmission simplifies driving operations and can reduce driving stress.
Comfort: The automatic transmission provides a smooth shifting experience without the frustration that may occur when shifting in a manual transmission, improving ride comfort.
Safety: Automatic transmissions help improve driving safety because drivers can focus more on observing and reaching road conditions.
Adaptability: The automatic transmission can automatically select the appropriate gear according to the vehicle’s driving conditions to optimize engine performance and fuel efficiency.
C. Disadvantages
High Cost: Automatic transmissions generally cost more to acquire and repair than manual transmissions.
Lower Fuel Efficiency: While the fuel efficiency of modern automatic transmissions has improved significantly, it is still not as good as a manual transmission in some situations, especially on economy vehicles.
Driving Experience: Some driving enthusiasts may think that the automatic transmission lacks driving pleasure and cannot provide direct feedback and control when shifting manually.
Weight Issue: Automatic transmissions are generally heavier than manual transmissions, which can have some impact on the vehicle’s performance and fuel economy.
D. Classification and Characteristics of Automatic Transmissions
According to different working principles, there are currently four types of automatic transmissions commonly used in automobiles, namely hydraulic automatic transmission (referred to as AT), mechanical continuously variable automatic transmission (referred to as CVT), electronically controlled mechanical automatic transmission (referred to as AMT), and dual-clutch automatic transmission (referred to as DCT).
1. Hydraulic Automatic Transmission (AT)
AT achieves automatic transmission through a combination of hydraulic transmission and planetary gears. It is generally composed of a hydraulic torque converter, planetary gear mechanism, shift actuator, shift control system, shift control mechanism, and other devices.
Advantages: Mature technology, high reliability, capable of carrying large torque, suitable for various driving conditions;
Disadvantages: The structure is complex and the maintenance cost is high;
It is suitable for vehicles requiring high reliability and durability.
2. Mechanical Continuously Variable Automatic Transmission (CVT)
The CVT uses a transmission belt and a main and driven wheel with variable working diameters to transmit power, which can realize continuous changes in the transmission ratio, thereby obtaining the best match between the transmission system and the engine working conditions.
The characteristic of the mechanical continuously variable automatic transmission is that the gear ratio is not a discontinuous point, but a series of continuous values, which can better coordinate the external driving conditions of the vehicle and the engine load, fully utilize the engine potential, and improve the vehicle fuel economy. It enables the vehicle to have loophole-free traction performance, thereby significantly improving the overall vehicle performance. At present, steel belt or chain transmission is mostly used for power transmission.
Advantages: It provides step-less and smooth shifting experience, good fuel economy, and simple structure;
Disadvantages: The torque it can withstand is relatively small, not suitable for high-performance or heavy-duty vehicles;
It is suitable for small cars or light vehicles.
3. Electronically Controlled Mechanical Automatic Transmission (AMT)
The electronically controlled mechanical automatic transmission is improved based on the traditional manual gear transmission. It is a mechatronic-hydraulic integrated automatic transmission that combines the advantages of both AT and MT; AMT has both AT and MT. The transmission has the advantages of automatic speed change but also retains the advantages of high efficiency, low cost, simple structure, and manufacturing of the original manual transmission gear transmission.
While the overall transmission structure of the mechanical gearbox remains unchanged, the automation of gear shifting is realized by adding a microcomputer-controlled automatic control system. Therefore, AMT uses an automatic shifting system to complete the process of operating the clutch and selecting and shifting gears.
Advantages: Improved based on manual transmission, low cost, high transmission efficiency;
Disadvantages: Shifting may feel frustrating, and the comfort is not as good as AT or CVT;
It is suitable for consumers seeking cost-effectiveness.
4. Dual-clutch automatic transmission DCT
The DCT uses two sets of clutches, and the two sets of clutches work alternately to achieve the effect of gapless shifting. DCT combines the advantages of AT and AMT, with high transmission efficiency, simple structure, and low production cost. It not only ensures the power and economy of the vehicle but also greatly improves the comfort of the vehicle.
Advantages: Works well with the hybrid system, providing a smooth driving experience and high fuel efficiency;
Disadvantages: The structure and working principle are relatively complex and only suitable for a small number of types of vehicles;
It is suitable for hybrid vehicles and consumers pursuing environmental protection and energy saving.
Different types of automatic transmissions have different applicable scenarios. When choosing, you should consider the following factors:
Driving Habits: whether you need to change gears frequently or prefer a smooth driving experience;
Vehicle Use: daily commuting or long-distance travel;
Economics: purchase cost, maintenance costs, and fuel efficiency;
Reliability: long-term operational reliability and ease of maintenance.
Each automatic transmission has its advantages and disadvantages, and customers should choose according to their actual needs.
About HONEST Automation
The picture shows our automobile transmission gear motor assembly line, which is equipped with functions such as manipulators, double-speed chain transmission, and assembly line pallet coding design. It has high production precision and a high degree of automation, ensuring the smooth progress of production operations. Our engineers will follow the equipment to the customer’s factory for installation and commissioning, so you can rest assured that the equipment will operate normally. If there are subsequent needs or questions, our engineers will also provide you with technical support at any time.
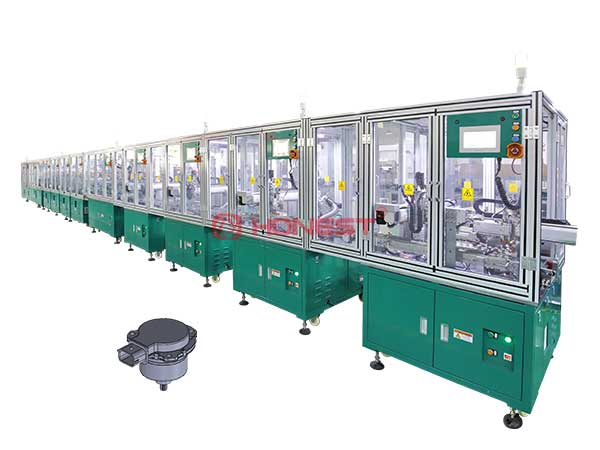

If you need more detailed information about our BLDC motor assembly line or production lines, please don’t hesitate to contact us at your convenience.






