Motors are devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, enabling either rotational or linear motion. Based on their function, they can be categorized into drive motors and control motors. Among them, coreless DC motors and frameless torque motor are key types of control motors widely used in precision applications.
In recent years, national policies have actively supported the development of the motor and automation industries. As one of the core components of humanoid robots, the motor plays a crucial role in achieving breakthroughs in advanced motion control technologies. In the near future, as humanoid robots move toward large-scale mass production, the demand for high-performance motors—especially coreless and frameless torque motors—is expected to grow significantly.
01 Overview of the Motor Industry
1.1 Motor Classification and Differences
A motor is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, generating either rotational or linear motion. Its operating principle is based on electromagnetism, where current interacts with a magnetic field to produce motion. Motors are an essential part of modern engineering and technology, playing a key role in mechanical drive, power transmission, and control systems. With continuous technological advancement, motor performance and efficiency have steadily improved to meet the needs of various applications.
Motors come in a wide variety of types and can be classified according to different criteria. Based on the power supply, motors are divided into DC motors and AC motors. DC motors are powered by a direct current source, while AC motors are powered by an alternating current source.
(1) DC Motors
A DC motor is a device that converts direct electrical energy into mechanical energy. It offers advantages such as stable speed, high starting torque, and high efficiency, but its drawbacks include a complex structure, difficult maintenance, and higher cost. DC motors are commonly used in machine tools, robots, electric vehicles, and ships. Structurally, they are classified into brushed DC motors and brushless DC motors.
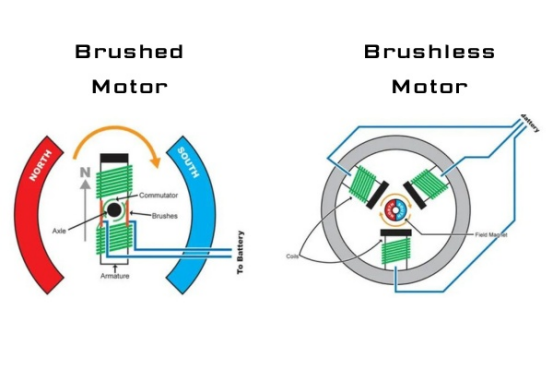
Brushed DC Motors
Brushed DC motors use mechanical commutation, with fixed magnetic poles and a rotating coil. During operation, the coil and commutator rotate, while the magnets and brushes remain stationary. The reversal of the coil current is achieved through the commutator and brushes rotating with the motor.
Brushed DC motors feature a simple structure, mature technology, and relatively easy manufacturing, and they have been widely applied in various fields. In addition, they offer high starting torque, fast response, and precise control, with control accuracy reaching up to 0.01 millimeters.
Brushless DC Motors
Brushless DC motors use electronic commutation, with stationary coils and rotating magnetic poles. The motor detects the position of the permanent magnet poles through Hall sensors and switches the coil current at the appropriate time to generate magnetic forces in the correct direction, driving the motor.
By eliminating brushes, brushless DC motors experience reduced bearing wear, resulting in longer service life and lower maintenance costs. Additionally, reduced friction during operation ensures smoother performance and lower noise levels.
Based on their application, motors can be classified into drive motors and control motors.
Control Motors
Control motors are primarily used for precise speed and position control, functioning as actuators within control systems. They can be further categorized into stepper motors, servo motors, and torque motors.
Stepper Motors
A stepper motor is an actuator that converts electrical pulse signals into angular displacement. When the stepper driver receives a pulse signal, the motor rotates a fixed angle in the specified direction. By controlling the number of pulses, the angular displacement of the motor can be precisely managed, achieving accurate positioning. Additionally, the motor's speed and acceleration can be controlled by adjusting the pulse frequency. Stepper motors feature a simple structure, high reliability, and low cost, making them widely used in applications such as automatic feeders and printers.
Servo Motors
A servo motor converts an input voltage signal into mechanical output at the motor shaft, driving the controlled component to achieve precise control. Servo motors are typically equipped with encoders that provide feedback to the driver. The driver compares the feedback with the target value and adjusts the rotor’s rotation accordingly. Due to their high precision, fast response, strong stability, and ability to generate significant output torque, servo motors are widely used in various control systems.
Torque Motors
A torque motor is a type of motor primarily designed to control output torque. Its control focus is on precise regulation of torque rather than motion direction. Due to their high torque output and precise control capabilities, torque motors are widely used in applications requiring high dynamic performance, precise positioning, and stable torque output, such as machine tools, automated production lines, and robot joints. Structurally, torque motors can be classified into frameless brushless motor and cased torque motors.
02 Coreless DC Motors
2.1 Classification and Differences of Coreless DC Motors
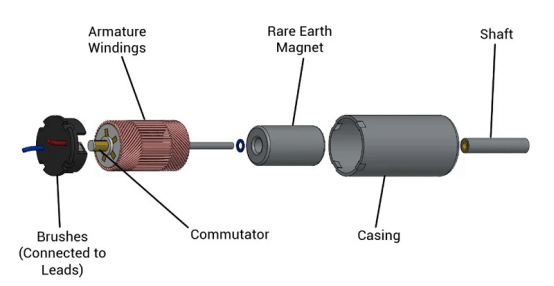
A coreless DC motor is a direct-current permanent-magnet servo motor with a rotor that has no iron core. Its main components include the shaft, bearings, brushes, commutator, cup-shaped winding (rotor), rotor shaft, coils, sliding bearings, housing, and magnets (stator). One distinctive feature is the slotted cross-section of the ring-shaped magnets, which are magnetized in the radial direction.
Coreless DC motors offer remarkable energy efficiency, responsive and convenient control characteristics, and stable operation, reflecting their advanced technology. The torque generated by the motor is evenly distributed, ensuring smooth performance at low speeds and reducing vibration and noise at high speeds.
Based on the commutation method, coreless DC motors can be classified into brushed coreless motors and brushless coreless motors.
Brushed Coreless Motors
Brushed coreless motors feature a simple structure and relatively low cost. Electrical energy is converted into mechanical energy through the contact between brushes on the rotor and the commutator. This contact generates sparks and, during wear, produces some noise and vibration, which can also affect motor performance and shorten its lifespan. Brushed coreless motors are suitable for applications with lower requirements for size and weight, such as small household appliances.
Brushless Coreless Motors
Brushless coreless motors have a more complex structure and higher cost. Without brushes or a commutator, they use electronic commutation to convert electrical energy and automatically adjust the current direction based on the rotor position, allowing spark-free operation, reducing energy loss, and extending motor lifespan. Brushless coreless motors are compact and lightweight, offering high efficiency and long service life, making them ideal for applications such as drones, robots, and precision equipment.
2.2 Expanding Downstream Applications and High Industry Barriers
The upstream of the coreless DC motor industry chain includes raw materials and components. Key raw materials are copper, steel, and permanent magnet materials, while components mainly include bearings, castings, and plastics. The midstream consists of coreless DC motor manufacturers, whose manufacturing processes feature coil windings in linear, saddle-shaped, and skewed configurations.
Downstream applications cover robots, aerospace, consumer electronics, and more. Coreless DC motors were initially used in aerospace, with their application areas gradually expanding over time. In 2023, the top five downstream applications in China were medical devices (37%), warehousing and logistics (15%), industrial automation (12%), aerospace (11%), and robots (8%).
Technical Barriers
Regarding technical barriers, the manufacturing process of coreless DC motors is complex, with the core technology concentrated on the coil windings. The coil winding process directly affects critical performance parameters such as motor size, speed, power density, and yield. Compared to conventional brushless, brushed, and servo motors, coreless DC motors feature a slotless structure with no stator slots; the enamelled wire is wound in a suspended manner without any internal support, making the production process highly challenging.
In terms of winding precision, coreless DC motors require higher accuracy than traditional motors. Due to their compact size, they have a lower tolerance for errors, and manufacturing precision directly affects the stability of the magnetic field. Variations in wire gauge and the number of winding turns can lead to significant differences in coil resistance, starting current, and speed constants. Therefore, it is essential to enhance manufacturing precision and yield during production.
Barriers to Customized Products
For customized products, the quality of coreless DC motors directly impacts the performance and system stability of downstream customer products. Manufacturers often need to adjust motor design and production processes according to specific customer requirements. Another approach involves forming strategic collaborations with customers, which creates strong customer loyalty and makes it difficult for new entrants to penetrate the market, thus establishing significant barriers.
Financial Barriers
Regarding financial barriers, coreless DC motors are compact and require high-precision control, which imposes stringent process requirements. Manufacturing them demands significant investment in modern equipment, such as fully imported high-precision molds, fully automated high-speed punching machines, automatic stator plating equipment, precision rotor production lines, and automated production lines. Moreover, product updates and iterations require sufficient capital to support subsequent equipment investments and research and development costs.
2.3 High Industry Concentration and Growing Market Potential
The global coreless DC motor market is primarily dominated by overseas companies, resulting in a high market concentration. Coreless DC motors feature high technological content and complex manufacturing processes. As downstream applications continue to expand and product performance varies, manufacturers must possess certain customized production capabilities to meet customer requirements. Additionally, due to rapid technological updates, manufacturers need to continuously optimize and upgrade their products.
Currently, the global coreless DC motor market remains dominated by foreign manufacturers, with overseas companies holding an 85% market share in 2023. With strong technological accumulation, leading overseas companies contributed to a CR5 of 67% in 2022. The top five global manufacturers are Faulhaber, Portescap, Allied Motion Technologies, Maxon Motor, and Nidec Copal Corporation.
The downstream applications of coreless DC motors are expanding rapidly, with market potential continuing to grow. On one hand, increasing demands for precision and speed in medical devices, aerospace, and industrial automation are driving the continuous expansion of the coreless DC motor market. On the other hand, coreless DC motors, with their fast response and high-precision characteristics, are highly suitable for humanoid robot hand joints. With the mass production of humanoid robots, this emerging market is expected to further boost the overall market size of coreless DC motors.
Humanoid Robots Unlock Market Potential
According to the Research Institute, assuming each humanoid robot is equipped with a pair of five-fingered dexterous hands (taking Tesla’s humanoid robot as an example), a total of 12 coreless DC motors are used per robot. Considering factors such as mass production and technological updates, the average unit price is expected to decline annually. With annual production volumes of 50,000, 1,000,000, and 5,000,000 humanoid robots, the global market for coreless DC motors is projected to reach CNY 1.083 billion, CNY 20.577 billion, and CNY 97.741 billion, respectively. In China, the corresponding market sizes are expected to be CNY 542 million, CNY 10.289 billion, and CNY 48.870 billion, respectively.
03 Frameless Torque Motors
3.1 Mainstream Motors for Humanoid Robot Joints: Evolving Towards High Performance and Diverse Applications
Frameless torque motors consist of a stator and a rotor, lacking the traditional motor housing and bearings. They can be directly integrated into equipment, enabling a compact design and efficient power transmission. Characterized by high torque at low speeds, they eliminate intermediate mechanical transmission components, reducing energy loss and system inertia while enhancing dynamic response and positioning accuracy. Frameless torque motors are widely used in industrial automation, robots, aerospace, and medical devices.
Frameless torque motors feature compact size, high power, and high torque output at low speeds, making them the mainstream choice for humanoid robot joint drives. Compared with conventional motors, frameless torque motors better meet the performance requirements of humanoid robots. Their hollow design reduces the space occupied, supporting the trend toward lighter robots, while enabling greater torque output at low speeds. Additionally, their performance remains stable under high-voltage or high-temperature conditions, making them an ideal choice for humanoid robot joint actuation.
From a technical barrier perspective, the core challenges for frameless torque motors lie in magnetic circuit design and manufacturing processes. Torque density and power density are critical factors affecting robot performance. Since frameless torque motors must deliver high power under low-voltage conditions, they impose stringent requirements on magnetic circuit design and production techniques.
Looking ahead, with the rapid development of downstream industries and continuous product iteration, frameless torque motors are expected to evolve towards high performance and multi-application scenarios. In terms of high performance, optimizing the electromagnetic structure and materials can increase torque output per unit volume or weight, meeting the needs of compact downstream designs. For multi-application scenarios, developing specialized frameless torque motors for different downstream sectors will further enhance adaptability and stability.
The upstream segment of the frameless torque motor industry chain mainly includes neodymium-iron-boron magnets, steel, and winding equipment. The midstream consists of frameless torque motor manufacturers, while downstream applications cover robots, general machinery, medical devices, and aerospace. In China, robots account for 80% of downstream applications, with sub-segments including collaborative robots and humanoid robots.
3.2 Fragmented Market Structure: Humanoid Robots Expand Market Potential
Overseas manufacturers started earlier, enjoying a first-mover advantage in technology and production processes. Major international frameless torque motor manufacturers include Copley (USA), TQ-RoboDrive (Germany), Aerotech (USA), and AVS Mechatronics GmbH (Austria). With deep technological accumulation, these companies hold leading positions in R&D and manufacturing processes. For example, Copley products use distributed slot designs and carbon fiber winding techniques, while TQ-RoboDrive products employ modular stators and epoxy potting. In contrast, domestic manufacturers started relatively late and still lag behind in torque density and high-end frameless torque motor products.
Products are mainly customized, and the market is fragmented. Although robots are the largest downstream application for frameless torque motors, different types of robots—such as collaborative robots, industrial robots, quadruped robots, and humanoid robots—have varying requirements for motor parameters, making customization the dominant approach.
Driven by demand from the humanoid robot industry, the market for frameless torque motors is on the rise. According to a research institute, the global market for frameless torque motors will be approximately US$657 million in 2023. With the mass production of humanoid robots, demand is expected to increase further. The global market for frameless torque motors is projected to be approximately US$903 million in 2030, with a compound annual growth rate of 4.65% from 2023 to 2030.
04 Technical Barriers and Future Outlook
Currently, next-generation dexterous hands are attracting significant attention. As a key component of these hands, coreless DC motors are expected to achieve higher precision and improved performance in the future, enabling dexterous hands to perform fine tasks such as playing the piano or threading a needle. Frameless torque motors, as the mainstream solution for linear and rotary transmission, offer clear advantages. With the continuous expansion of downstream applications, incremental demand is expected to grow. In the future, as humanoid robots gradually move toward industrialization, with companies like Tesla and UBTECH Robotics leading successful mass production, the market potential for coreless DC motors and frameless torque motors is set to expand significantly.
Honest Automation provides comprehensive assembly solutions for humanoid robots, including joint motor assembly equipment, frameless torque motor assembly, coreless DC motor assembly, and winding machines. The company has successfully collaborated with leading global manufacturers of humanoid robots and has delivered mature assembly solutions for automotive-grade brushed motors, brushless motors, and hairpin motors in the automotive and automotive parts industries. We welcome you to consult online for free customized solutions or to schedule a visit.






