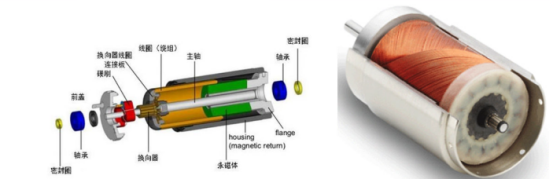
What Is a Coreless Motor?
A coreless motor is a type of ironless-wound motor, also known as a “slotless motor” or “ironless core motor.”
Its main distinction lies in the use of cup-shaped windings instead of the conventional iron-core windings. These self-supporting cup-shaped windings can serve as either the stator or rotor, enabling lightweight construction, low inertia, and high dynamic response.
This design eliminates the traditional teeth and slots found in conventional motors, significantly reducing magnetic cogging and torque ripple, lowering energy loss, and greatly enhancing motor performance.
In short, a coreless motor is essentially a motor without the traditional iron core.
Coreless Motor Market Heats Up with Rapid Expansion of Applications
In recent years, driven by the commercialization of humanoid robots, supportive low-altitude economy policies, and the miniaturization of medical devices, the application scope of coreless motors has expanded rapidly, with growing market demand.
According to multiple industry reports, coreless motors are experiencing rapid growth, with a compound annual growth rate significantly higher than that of traditional motor types. In the humanoid robot sector, a single device may require dozens of high-dynamic micro-motors, making them a key driver of market expansion.
Moreover, in applications such as medical devices, drone gimbals, and AR/VR optical systems—where size, noise, and response speed are critical—coreless motors are shifting from an optional choice to a necessity. This technology migration, driven by downstream demand, is attracting increasing attention from companies looking to enter this market segment.
Behind all of this lies a common challenge: how to take these high-performance motor designs out of the lab and into mass production?
To address this, we must return to the “core structure” of the coreless motor—the windings.
Coil Windings: Determining Performance and Manufacturability
If the iron core is the “skeleton” of a traditional motor, the windings are the “entire structure” of a coreless motor. Windings not only carry current to generate driving force but also must maintain structural stability, while affecting heat dissipation and dynamic balance.
Currently, the industry commonly uses three main types of windings:
Linear Windings
Linear windings feature wires wound in a straight line along the motor axis, forming a cylindrical-like structure. The end coils are typically thicker. While this design is relatively simple to manufacture, the larger end volume results in lower effective space utilization.
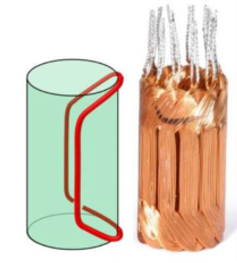
Diamond/Saddle-Shaped Windings
These windings are shaped like a “saddle,” closely conforming to the inner surface of the magnets and arranged compactly, allowing for higher copper fill ratios. Optimized magnetic flux paths enable magnetic efficiency exceeding 90%, resulting in low energy loss and high efficiency—especially suitable for high power density and long-life applications.
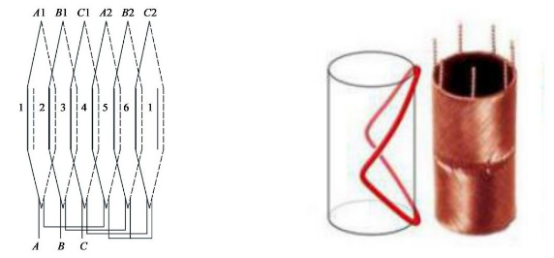
Helical Windings
Helical windings feature wires wound diagonally along the circumference, forming a spiral structure. The end sections are smaller, making the overall winding more compact. This design helps reduce the motor’s axial length and improves compatibility with automated winding equipment, enabling high-speed, high-consistency mass production.

It is worth noting that the more complex the winding type, the higher the requirements for subsequent assembly processes. For example, saddle-shaped windings, due to their compact arrangement, require precise tension control during assembly to maintain shape consistency, while helical windings demand higher accuracy in the motion paths and positioning of the winding equipment.
These details often determine the yield and stability of the final product.
Different sizes not only determine the application scenarios of coreless motors but also directly influence the design of the entire assembly process. This means that each coreless motor is essentially a new engineering challenge, requiring targeted solutions.
Once the technical core of the coreless motor is clarified, a fundamental question arises: how can these intricate designs be reliably transformed into high-quality, mass-produced products?
The root of the challenge lies in the conflict between the unique structural characteristics of coreless motors and mass production:
Their ironless design results in weaker self-supporting windings, which can deform, shift, or even break during assembly. At the same time, high-density windings (such as saddle-shaped or helical types) demand extremely precise tension control, positioning accuracy, and process stability.
The more immediate challenge is:
(1) Manual winding struggles to ensure consistency, leading to significant yield fluctuations.
(2) Semi-automated equipment is complex to adjust and difficult to reconfigure, making it unsuitable for multi-model, small-batch production.
(3) Continuous miniaturization of motors imposes extreme challenges on traditional clamping and inspection methods.
These common challenges across the industry have made companies realize that simply adding manpower or relying on generic equipment can no longer meet the strict requirements of humanoid robots for performance consistency, traceability, and on-time delivery.
For coreless motors with compact structures and complex processes, adopting advanced automated assembly is no longer just a cost-efficiency decision; it has become a critical requirement for companies to reliably deliver high-quality products and successfully enter the coreless motor market.
The wave of coreless motors has arrived, representing the future of precision power drives. Yet, a “manufacturing gap” lies between outstanding design and stable mass production.
While Honest Automation does not directly manufacture coreless motors, we possess deep insight into every technical detail, process nuance, and market trend. Our mission is to transform this expertise into the most reliable and efficient automated assembly solutions for your production needs.
This “bridge” is built on a manufacturability assessment system, a flexible automation platform, and process data validated by millions of automotive motors.
Now, let’s start a discussion based on your specific needs, transforming your coreless motor concepts into mass-producible, deliverable, and market-leading products.







