“E-Bike” has become a popular term worldwide in recent years. It originates from “Electric Bicycle,” referring to bicycles equipped with an electric assist system — commonly known as pedal-assist bikes. Different countries set their own regulations for rated motor power and maximum assisted speed. Under EU standards, the motor power must not exceed 250 W, and the assist function must automatically shut off once the speed reaches 25 km/h.
The global surge of E-Bikes has rapidly swept across Europe, the United States, and Japan over the past few years. As a result, E-Bikes have become one of the fastest-growing segments in the bicycle industry. The market continues to expand at an annual growth rate of over 30%, making it a major driving force behind the industry’s sustained momentum.
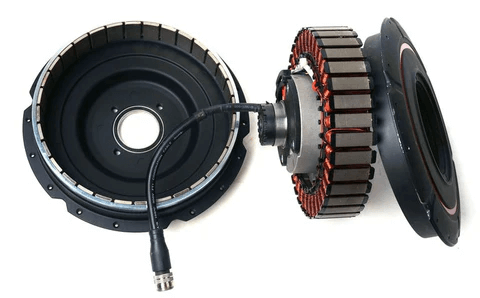
Leading international brands such as SHIMANO have launched dedicated drivetrain and braking systems for E-Bikes and have even expanded into complete motor product lines. Other well-known manufacturers, including NECO, are also actively developing E-Bike drive motors.
Within this booming market, the core of pedal-assist technology lies in the motor system itself, along with essential components such as sensors and drivetrain mechanisms. Companies that master these key technologies gain a decisive advantage and can effectively influence the future direction of the E-Bike industry.
In traditional electric bicycles, the power system is typically integrated into the wheel hub, commonly known as a hub motor. However, modern high-performance E-Bikes have significantly evolved in design: the battery is often concealed inside the downtube, while the motor is neatly positioned at the bottom bracket area.
This type of motor—which replaces the bottom bracket and incorporates a built-in gear reduction unit—is widely referred to as a mid-drive motor. Today, mid-drive systems have become the preferred solution for mid- to high-end E-Bikes, dominating the best-selling models in Europe and the United States.
Why are mid-drive motors considered the most optimal pedal-assist solution? Compared with hub motors and earlier designs, mid-drive systems offer more advantages: lighter weight, higher efficiency, and a far more natural and responsive riding experience. As a result, they have become the first choice for many leading brands.
A full technical analysis of mid-drive motors could easily take days, but in summary, the key benefits of using a mid-drive motor in an E-Bike include the following:
1. Lower Resistance and Reduced Rolling Drag with Mid-Drive Motors
Traditional hub motors are typically brushless motors that operate using magnetic induction and regulate speed by controlling current. Their design is relatively simple, but due to inherent structural limitations—such as rotational friction and heat buildup—the overall efficiency tends to be lower. Most hub motors convert only about 70–80% of electrical energy into mechanical power.
Another well-known drawback of hub motors is magnetic drag, often referred to as cogging drag. As the battery depletes, the internal electromagnetic resistance increases. This makes riding without power significantly harder, and the drag becomes more noticeable the longer you ride.
Mid-drive motors, however, avoid this issue entirely due to their different drivetrain architecture. They generate far less rolling resistance, and pedaling without electric assist remains relatively effortless.
Mid-drive motors deliver power directly to the bottom bracket and rely on components such as a clutch mechanism, drive shaft, and reduction gears to transfer torque to the chainring, providing pedal assistance. Because the motor engages directly with the mechanical drivetrain, the conversion efficiency from electrical to mechanical energy commonly exceeds 80%, making it significantly more efficient than typical hub motors.

Most mid-drive systems also incorporate a freewheel clutch inside the motor. This allows the motor to completely disengage from the crankset when the system is not powered, eliminating magnetic drag entirely. As a result, riders can pedal smoothly during regular fitness riding or even when the battery is fully depleted, without experiencing additional resistance.
2. More Gear Options and Higher Torque Output with Mid-Drive Motors
Even with the addition of a torque sensor, traditional hub motors still rely primarily on adjusting current to control speed. To generate more load capacity or climbing torque, the motor must simply spin faster. This approach leads to higher power consumption and significant wasted energy, resulting in overall lower efficiency.
Advanced mid-drive motors employ a multi-stage internal gear reduction system, using a series of clutch gears and ratchet mechanisms inside the motor housing to achieve higher torque output. This design greatly improves load capacity and climbing performance. In addition, the torque sensor in a mid-drive system is far more responsive, detecting even subtle changes in pedaling force at the crank and delivering immediate acceleration feedback.
Because mid-drive motors do not alter the bicycle’s original drivetrain layout, riders can still use the existing rear mechanical gearing in combination with the mid-drive assist. This coordination enables significantly higher pedaling efficiency and better overall riding performance.
3. Better Weight Distribution and Superior Handling with Mid-Drive Motors
In earlier E-Bike designs, hub motors—whether mounted on the front or rear wheel—add substantial mass directly to the wheel, resulting in poor weight distribution. Manufacturers often had to rely on battery placement to counterbalance the uneven load caused by the motor.
When a hub motor engages, the power is applied directly to the wheel, creating noticeable drag and jerky acceleration, especially during startup. This reduces ride smoothness and makes precise bike control more difficult.
Concentrating most of the added weight at the wheel also affects braking performance. The increased rotational inertia from the motor places extra load on the braking system, reducing responsiveness and overall handling stability.
As the name suggests, a mid-drive motor is mounted at the center of the frame, keeping the bike’s center of gravity low and balanced. This design does not compromise stability at high speeds and eliminates the need for additional battery weight to balance the bike. Consequently, most modern E-Bikes place the battery inside—or even fully integrated within—the downtube.
Moreover, a mid-drive motor delivers power exclusively through the bottom bracket–crankset–chainring system. Pedaling feels natural, and riders can continue to operate the mechanical drivetrain as usual, selecting different gear ratios to suit varying terrain and riding conditions. This makes mid-drive systems particularly well-suited for performance-oriented bicycles.
In addition, mid-drive motors do not add extra load to the braking system. With no added weight at the wheels, standard braking performance remains unaffected.
4. Fewer Wires, Simplified Accessories, and High Integration with Mid-Drive Motors
Another major advantage of mid-drive motors is their high level of integration. All sensors are built into the motor housing, with only a single wire extending to the handlebar controller. Even the battery connection is often routed internally through discreet wiring and contact points. This streamlined, integrated design makes maintenance easier, gives the bike a cleaner appearance, and provides a more convenient user experience.
5. Superior Dust and Water Protection, Low Failure Rate
Recent mid-drive motor solutions, such as the MM18 model by NECO showcased at the White Dove Action Expo, feature a highly integrated design. In addition to the previously mentioned clutch and drive gears, the motor housing also incorporates a torque sensor and a speed sensor.
The motor enclosure generally provides excellent protection, typically rated at IP65 or higher. During operation, the motor is fully resistant to dust and debris and can withstand low-pressure water jets from any angle. This robust design significantly reduces the risk of failure and enhances overall bike reliability.

In contrast, traditional electric-assist systems often rely on claw-type torque sensors or externally mounted bottom bracket torque sensors, along with separately installed speed sensors on the frame. The large number of external components increases the likelihood of malfunctions during everyday use.
E-Bikes are shaping the future of cycling by reducing rider effort and enhancing the overall riding experience. Technological progress relies on continuous investment in R&D, with manufacturers competing to deliver superior innovations. Amid this rapid wave of development, we look forward not only to new mid-drive motor technologies but also to even greater breakthroughs in the future. Convenience and enjoyment are within reach—why not experience firsthand the new sensations and fun that E-Bikes bring?
Honest Automation offers customized solutions for mid-drive motors. Due to the complex structure of mid-drive motors, their assembly presents significant challenges, and only a few manufacturers can provide automated assembly equipment. We have successfully developed and delivered fully automated mid-drive motor assembly lines, enabling highly efficient and stable production. Interested customers are welcome to contact us for more information or visit our facility for an on-site demonstration and consultation.






