1. What is Coreless Motor Winding?
Coreless motor winding refers to the precision winding process used in manufacturing coreless DC motors — a type of permanent magnet servo motor widely applied in robotics, medical devices, and precision instruments. Unlike traditional iron-core motors, the coreless motor adopts a cup-shaped, ironless coil (air-core winding) structure that completely eliminates the iron core from the rotor or stator.
This innovative winding structure effectively avoids eddy current losses and magnetic hysteresis, significantly improving energy conversion efficiency. By using fine copper wire and high-precision coil winding technology, the rotor achieves lightweight construction, low inertia, and rapid response, allowing excellent dynamic performance and smooth operation even at high speeds.
In addition, the winding accuracy and balance of the coreless rotor play a decisive role in reducing vibration and noise, improving the reliability and lifetime of the motor. Through optimized winding tension, coil layering, and automated winding processes, manufacturers can achieve highly consistent quality and production efficiency.
With its high energy efficiency, sensitive control, and smooth motion characteristics, coreless motor winding technology represents the advanced direction of precision motor manufacturing and continues to drive innovation in emerging fields such as humanoid robots, drones, and micro-actuators.
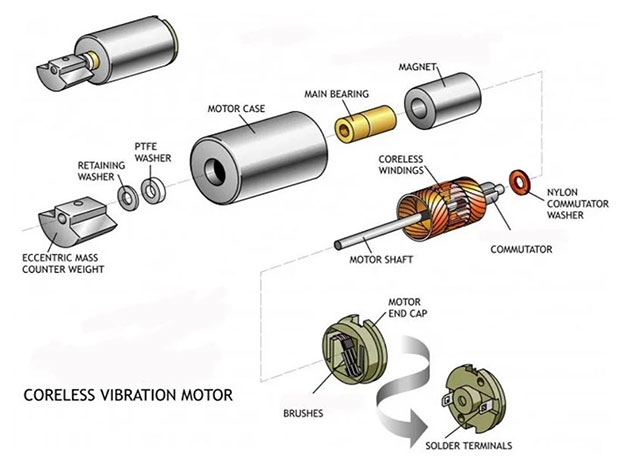
2. Advantages of Coreless Motors
Compared with traditional servo motors, coreless motor eliminate the iron core structure, which essentially solves the inherent problems of the iron core structure. The losses of iron core motors are divided into four categories: stator winding copper loss, stator iron loss, rotor air friction loss and rotor eddy current loss. Stator iron loss (including hysteresis loss, classic eddy current loss and abnormal eddy current loss) and rotor eddy current loss can be avoided by eliminating the iron core structure of the stator or rotor. The size of the stator winding copper loss is affected by many factors such as the motor operating frequency, the size of the winding conductor and the arrangement position in the slot, so it is also affected by the elimination of the iron core structure. The rotor air friction loss is proportional to the cube of the motor speed, so the wind wear of the rotor accounts for a large proportion in high-speed motors. If the rotor is replaced with a coreless structure, that is, a cup-shaped self-supporting coil, it is small in size and light in weight and can achieve smaller wind wear at high speeds. The iron core motor has a large loss caused by the structure, especially under high speed conditions. The design structure of the coreless motor determines that its characteristics can avoid various problems of the iron core motor.
Comparing the coreless motor with the traditional iron core motor, it can be found that the coreless motor has many advantages due to its novel structural characteristics: no hysteresis, small electromagnetic interference, and can reach extremely high motor speed. Since there is no iron core in the rotor structure, there is no cogging effect, so the corresponding iron loss is small. The energy conversion efficiency is extremely high, and the energy utilization rate is 75%~90%. The small inertia motor rotor can achieve faster acceleration, has excellent dynamic response performance, has good starting and braking performance, faster response speed, and smaller mechanical time constant. Some products can reach less than 10ms. Under high-speed operation, the speed adjustment is sensitive and has more reliable operation stability. The energy density of the coreless motor is much greater than that of other motors, and the weight can be reduced by half compared with the iron core motor of the same power.
3. Coreless Motor Classification
Brushed coreless motor and brushless coreless motor
Coreless motors can be divided into brushed coreless motors and brushless coreless motors according to the commutation method. The difference between brushed and brushless coreless motors is the working mode of the stator and rotor and whether there is a commutator.

The structures of brushless motors are different:
Brushed coreless motor: The main parts include coreless motor coil with commutator, permanent magnet, commutation brush and commutation brush bracket. The commutator uses mechanical brushes, the permanent magnet is the stator, and the coreless motor coil is the rotor.
Brushless coreless motor: The main parts include coreless motor coil, permanent magnet rotor and Hall sensor PCB. Among them, the commutator uses Hall sensor to detect the rotor magnetic field signal, converting mechanical commutation into electronic signal commutation, further simplifying the physical structure of the coreless motor. The rotor of the brushless coreless motor is a permanent magnet and the stator is a coreless motor coil.
Brushless coreless motor have better performance in terms of speed, weight, power-to-volume ratio, etc.
Compared with brushed coreless motor, brushless coreless motor have better performance, higher speed limit, smaller weight, and higher power-to-volume ratio, but the price is relatively high.
4. Core Parts
The main parts of the coreless motor include coreless motor coil, housing, bearing, lower shell, upper shell, permanent magnet, etc. Among them, the key part of the coreless motor is the coreless motor coil, which has no other supporting structure and is completely wound by wire. The shape design, arrangement neatness, winding slot full rate and other factors of the coreless motor coil are the key factors that determine the performance of the coreless motor.
5. Core technology barriers
The overall assembly process of the coreless motor is similar to that of an ordinary motor, and its core technical barrier lies in the self-supporting winding technology of the stator/rotor.
The key to achieving self-supporting winding lies in the design of the winding process.
There are many types of windings for coreless motors, including disc winding, straight winding, oblique winding, concentric winding, stacked winding, etc.
The effective conductor part of the direct-wound component is parallel to the armature axis, which belongs to concentrated winding. This winding method has a high slot filling rate, a thin wall in the middle of the winding cup, and because the enameled wire is not arranged neatly and stacked, the entire coreless motor coil is arranged in a messy way, and the end has a larger size due to the wiring margin at the end.
-
The oblique winding type is also called honeycomb winding. In order to be able to wind continuously, the effective side of the element needs to be at a certain inclination angle with the armature axis. This winding method makes the end size smaller. Since the oblique winding type requires a certain wire arrangement angle, the enameled wires overlap each other and the slot fill rate is low. Faulhaber uses oblique winding coils, which are wound and formed in one go by automated equipment, with a high pass rate, and the flatness and consistency of the winding cup are also very good.
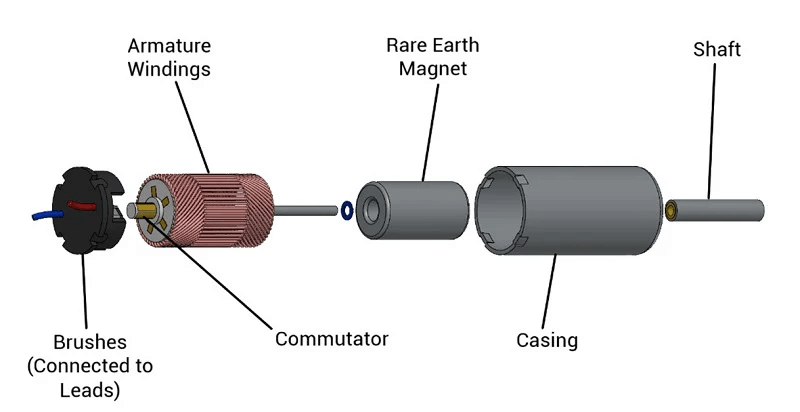
-
Concentric winding (diamond winding)
Concentric winding is also called diamond winding or saddle winding. It is a method of first winding into multiple single diamond coils and then arranging the wires. The coils generally use self-adhesive square wires for easy winding and fixing. Then, according to the product design size requirements, the single coil is shaped, and the formed coil is positioned with special tooling for annular fixing, and finally forms a cup shape. This method is convenient for controlling the size of the coreless motor after shaping and improving the slot fill rate. At the same time, it has high production efficiency and is suitable for mass production. The power density of the concentric winding coreless motor is relatively large. The Swiss Maxon motor uses a saddle winding method, and its motor product performance is excellent.
6. Application fields of coreless motors
Coreless motor are widely used in aerospace, medical, automation and other high-tech industries, it can be used in the following scenarios:
① The coreless motor can well meet the technical requirements of the follow-up system that needs fast response, such as the fast adjustment of the flight direction of missiles, the follow-up control of high-magnification optical drives, fast automatic focusing, highly sensitive recording and detection equipment, industrial robots, bionic prostheses, etc.
② Products that require stable and long-lasting dragging of driving components, such as various portable instruments, personal equipment, instruments and equipment for field operations, etc. For the same set of power supplies, the power supply time of the coreless motor can be extended by more than double that of the traditional DC motor.
③ Various aircraft, including aviation, aerospace, and aircraft models, can greatly reduce the weight of the aircraft by taking advantage of the light weight, small size, and low energy consumption of the coreless motor.
④ Optical instruments, medical equipment, subdivided applications include dental equipment, micro pumps, infrared lenses, pipetting modules, electric grippers, robot hands, dispensing valves, surgical tools, etc.
The application scenarios of coreless motor have gradually expanded from high-tech fields to civilian fields.
At present, coreless motors are mainly used in high-tech industries such as aerospace, medical, and industrial automation, and have gradually developed into civilian fields such as power tools. Coreless motors have the characteristics of high sensitivity, stable operation, and strong controllability, which meet the stringent requirements of high-tech fields for electric drives. Therefore, they are mainly used in high-tech fields such as aerospace, medical equipment, industrial automation, and robots. At the same time, coreless motors are also gradually used in civilian fields, such as office automation, power tools, etc.
HONEST Automation can provide brushed and brushless coreless motor winding machine assembly equipment. If you need corresponding automation equipment solutions, please leave a message to get customized solutions and expert advice.
Tel/WhatsApp/Wechat: +8618923732990
E-mail: sales@honest-hls.com






