Production Processes and Key Barriers of Coreless Motors
The production of coreless motors involves nearly 30 process steps: initial coil winding, installation of core components such as bearings, mandrels, and support rings in the mid-stage, and final-stage assembly, including end cover installation and PCB soldering. Among these, the most critical process is the manufacturing and winding of the coils, which encompasses three major technical barriers: coil design, winding processes, and winding equipment.
1. Coil Design
Coil design is the core of achieving a self-supporting winding in coreless motors and reflects a manufacturer’s deep understanding of motor design. Factors such as wire gauge and the number of winding turns directly affect key motor parameters, including winding resistance, startup current, and speed constant. These parameters, in turn, directly influence the motor’s reliability and operational performance, ultimately determining the quality of the coreless motor.
There are various types of windings for coreless motors, with the most common being three: straight-wound, skew-wound, and concentric (saddle-shaped) windings.
The straight-wound coil features wires parallel to the motor axis, forming a concentrated winding structure. The design process involves first winding standard enameled wire on a coil mold according to the required number of turns, then assembling the wires on a winding mandrel to form the coil, and finally curing the ends with adhesive. This winding method achieves a high slot fill factor and results in a thin middle wall of the winding cup. However, due to uneven wire arrangement and stacking, the coil distribution in the coreless motor tends to be irregular. This leads to less uniform electromagnetic force distribution compared with other winding methods, which can result in suboptimal efficiency or greater torque ripple during operation. Additionally, the straight-wound process is relatively complex, so its application in automated winding equipment is relatively limited.
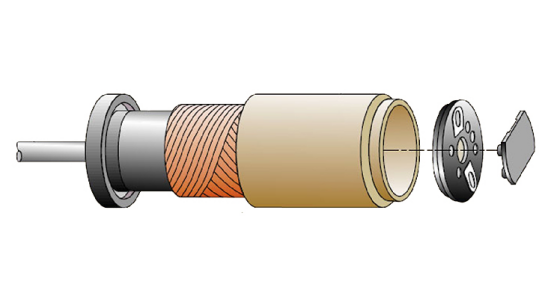
The skew-wound coil, also known as the honeycomb winding, requires the component’s effective edge to be set at a certain angle relative to the armature axis in order to achieve continuous winding. During the winding process, a specialized winding mandrel with two rows of pins is used. The mandrel rotates in sync with the winding machine, allowing the enameled wire to be neatly wound onto the mandrel. This method reduces torque ripple and enhances operational smoothness. One of the world’s top three coreless motor manufacturers, Germany’s Faulhaber, employs the skew-wound coil design in its motors.
The concentric winding, also known as the diamond or saddle-shaped winding, is first formed into multiple individual diamond-shaped coils and then arranged. Each coil is reshaped according to the product’s design dimensions, and the formed coils are fixed into a circular structure using specialized tooling, ultimately creating a cup-shaped winding. This method allows precise control of the final coreless motor cup dimensions, improves slot fill factor, and offers high production efficiency, making it well-suited for mass production. Swiss company Maxon Motor employs the saddle-shaped winding technique in its motors, achieving excellent performance in its products.
2. Coil Winding Processes
The coil winding process represents the second major technical barrier in coreless motor manufacturing. Coil winding methods can be divided into two types: semi-wound (stepwise) and one-shot automated winding. Internationally, the one-shot winding method is predominantly used, whereas in China, due to abundant and relatively low-cost labor, manual semi-wound production still occupies a significant proportion, resulting in lower efficiency and limited production line capabilities.
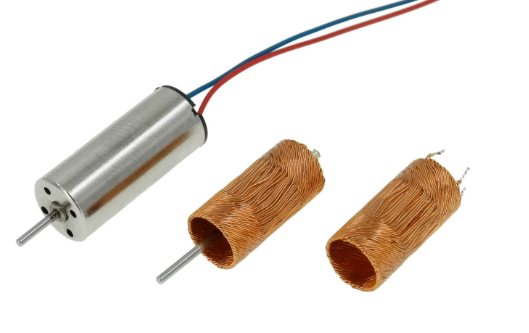
The semi-wound process generally involves two main steps: winding and coiling. First, the coil blank is wound on a winding machine. The blank is then taped and flattened, followed by coiling into a cylinder. The connection points are soldered, and the ends are joined to form a coreless motor coil. However, this method has limitations—it is mainly suitable for coreless motors with diameters of 20–30 mm and struggles with small coils where tap spacing is less than 7 mm, making it unsuitable for coreless motors with diameters below 10–12 mm.
In contrast, the one-shot production technology allows the winding machine to directly wrap the coil around the central axis in a single step. This method enables highly efficient automated production, simplifies the process, shortens production time, and significantly improves overall efficiency.
3. Coreless Motor Automatic Winding Machine
The level of winding equipment directly determines the achievable process quality, making the winding machine the third major technical barrier in coreless motor manufacturing. The main challenges lie in tension control for ultra-fine wires and winding under different coil designs.
A winding machine primarily consists of the frame, spindle assembly, wire arranging mechanism, tension control system, and molds. Because the wire is extremely fine—typically with a diameter of 0.02–0.25 mm—high-precision PLCs, servo motors, and transmission components are required. During wire feeding, excessive tension can stretch the wire, increasing its resistance, while insufficient tension can lead to loose winding and reduced coil quality.
At Honest Automation, we provide advanced solutions for coreless motor prototyping, winding machines, and assembly lines. Our equipment is designed to support high-precision, automated, and efficient production, meeting the diverse needs of coreless motor manufacturing.
Honest Automation offers flexible winding solutions suitable for a wide range of applications. Our systems enable precise control of coil winding, even at high speeds, ensuring consistent quality for high-performance coreless motor coils. With our comprehensive equipment and expertise, we can support both small-scale prototyping and full-scale production lines, helping clients achieve reliable and efficient motor manufacturing.
Welcome inquiries from motor manufacturers with coreless motor winding machines or prototyping needs. We offer customized solutions tailored to your specific requirements.
Tel/WhatsApp/Wechat: +8618923732990
E-mail: sales@honest-hls.com





