Robotic drive systems are generally categorized into hydraulic, pneumatic, and electric drive solutions. Among them, electric motor-driven systems are the most widely adopted, thanks to their high precision, fast real-time response, and ease of control. These advantages make electric drives particularly well suited to the development trends of modern robots, especially humanoid robots that demand precise and flexible motion control.
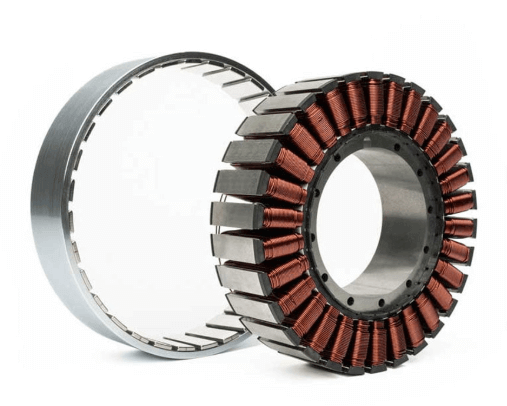
Frameless torque motors represent one of the most technically challenging motor categories, with high barriers in design, manufacturing, and system integration. As a result, the global market is characterized by a high level of concentration, with only a limited number of manufacturers capable of delivering high-performance, production-ready solutions. In China, only a small group of companies can provide frameless torque motors with consistent quality and reliability, including Inovance, Kollmorgen, Aerospace Electric, Haozhi Electromechanical, and Micro Precision Motor. On a global scale, leading manufacturers include Maxon Motor (Switzerland), MOOG, Sensata Technologies, Kollmorgen, and Novanta Group in the United States. Notably, Kollmorgen was among the earliest companies worldwide to develop frameless torque motor technology. In Tesla’s humanoid robot Optimus, frameless torque motors are used in all 14 linear actuators and 14 rotary actuators, enabling high-precision control while significantly reducing installation space.
Coreless motors, on the other hand, achieve a fundamental structural innovation by eliminating the traditional iron-core rotor and adopting an ironless, hollow-cup rotor design. This architecture completely removes eddy current losses associated with iron cores, while substantially reducing rotor mass and rotational inertia. As a result, mechanical energy losses are minimized and dynamic response performance is greatly improved. Due to these characteristics, coreless motors have become essential components in robotic dexterous hands and end-effectors. In the case of Tesla Optimus, each hand is equipped with six actuators, all of which utilize coreless motors to achieve highly responsive and precise finger-level motion control.
1.1 Frameless torque motors offer increased installation space, higher power density, and greater output torque, making them ideal for high-performance robots that require compact design and powerful actuation.
Torque motors are a type of specialized motor featuring flexible mechanical characteristics and a wide speed range. Key advantages include:
High torque at low speed: capable of delivering large torque even at low rotational speeds
High overload capacity: able to withstand short-term overloads
Fast dynamic response: excellent for precise motion control
High linearity and low torque ripple: ensures smooth and stable output
Unlike conventional motors, torque motors provide constant torque output rather than constant power. Their flexible mechanical behavior allows the motor to automatically reduce speed and increase torque when the load rises, protecting the system and maintaining stable operation. Typically, a torque motor is equipped with a speed feedback device on the shaft; combined with a controller, it automatically adjusts the terminal voltage to maintain stable torque output.
Torque motors can be categorized by their air gap structure:
Small air gap: suitable for general precision requirements, cost-effective
Medium air gap: performance superior to small air gap, smaller than large air gap motors, moderate cost
Large air gap: minimizes magnetic hysteresis and nonlinearity, delivers the lowest torque ripple and best linearity, but at higher cost
Torque motors are widely used in winding, unwinding, stepless speed control, and stall applications.
Frameless torque motors, a special type of torque motor, feature a frame-free design ideal for compact high-performance robotic joints. Advantages include:
Increased installation space: hollow design facilitates cable routing
Higher power density and torque: provides greater torque for the same motor size
Compact form factor: suitable for humanoid and collaborative robot joints
Direct load drive: eliminates the need for reduction gears, improving system accuracy
With the rapid development of artificial intelligence and collaborative robotics, service robots and precision humanoid robots require high responsiveness, high torque, and compact design in their joints. Frameless torque motors meet these requirements and can be customized to fit specific robotic joint architectures.
1.2 Frameless torque motors are an indispensable component of humanoid robots. Tesla's Optimus uses frameless torque motors in 28 actuators.
Frameless torque motors consist of only two core components—the stator and the rotor—without including a shaft, bearings, or end caps.
This architecture allows the motor to be directly coupled to the load by sharing the same bearing system, eliminating the need for separate shafts, bearing housings, end covers, and couplings typically found in conventional motors. As a result, system size, weight, and mechanical complexity are significantly reduced. At the same time, the direct-drive configuration improves servo stiffness and dynamic response performance.
Frameless motors can also be equipped with integrated Hall sensors and additional position feedback devices, such as encoders or resolvers, to form a complete closed-loop control system.
Thanks to their structural characteristics, frameless torque motors can be directly embedded into robotic mechanisms. The hollow-shaft design facilitates internal cable routing and enables highly integrated system layouts, helping reduce the overall size of the end product. In addition, frameless torque motors offer high torque output, stable performance, and high precision control.
In humanoid robots, frameless torque motors are considered one of the indispensable core components. They are widely used to drive joint motion and can also simulate muscle-like actuation. For example, Tesla’s humanoid robot Optimus utilizes frameless torque motors in its 14 linear actuators and 14 rotary actuators to achieve precise motion control while optimizing space utilization.
2.1 Compared to ordinary motors, coreless motors have higher power density, higher efficiency, higher precision, and higher integration.
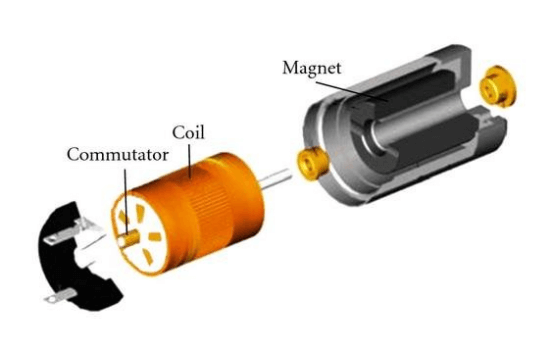
Definition and Working Principle of Coreless Motors
Coreless motors are a type of DC permanent magnet servo motor and are often classified as specialty micro motors. Structurally, they differ fundamentally from conventional motors by adopting an ironless rotor design, commonly referred to as a hollow-cup rotor.
This innovative rotor structure completely eliminates eddy current losses and iron losses associated with traditional iron-core rotors. As a result, coreless motors typically achieve higher efficiency than conventional micro DC motors. Since the winding itself forms the rotor, the rotational inertia is extremely low, enabling excellent dynamic response and precise controllability.
However, due to the absence of an iron core, the rotor winding must be designed very thin; otherwise, magnetic flux losses would occur. Consequently, the output power of coreless motors is relatively limited, and even large-size coreless motors typically deliver only several hundred watts.
Structural Differences Between Coreless Motors and Conventional Motors
Different rotor structures
Coreless motors use a hollow-cup, ironless rotor, whereas conventional motors employ solid iron-core rotors.
More compact dimensions
The hollow structure allows coreless motors to achieve a more compact form factor. For the same power output, a coreless motor generally occupies less volume than a conventional motor.
Lightweight design
The ironless architecture significantly reduces weight, making coreless motors ideal for weight-sensitive applications.
Application Advantages of Coreless Motors
High power density
Due to their compact size, coreless motors offer higher power density, delivering greater power output per unit volume.
High efficiency
Short magnetic paths and reduced iron and copper losses result in superior energy conversion efficiency.
High precision control
When combined with high-resolution encoders, coreless motors enable highly accurate position and speed control.
High level of integration
Coreless motors often integrate sensors such as encoders, allowing real-time monitoring of rotor position and speed for advanced motion control.
2.2 Coreless motors are widely used in aerospace, medical devices, industrial automation, and robotics applications.
A coreless motor typically consists of a rear cover, terminals, brush end cap, brushes, commutator, cup-shaped winding (rotor), shaft, washers, sleeve bearings, housing, magnets (stator), flange, and positioning ring.
The stator is composed of permanent magnets, a housing, and a flange. The housing and magnets together provide a constant magnetic field. Thanks to the ironless design, coreless motors eliminate iron losses and do not exhibit soft magnetic teeth or cogging effects. As a result, the generated torque is highly uniform, ensuring smooth operation even at low speeds.
At higher rotational speeds, coreless motors exhibit reduced vibration and lower noise levels, making them suitable for applications requiring quiet and stable operation.
The rotor consists of windings and a commutator. The windings are connected to the shaft via the commutator and rotate within the air gap between the magnets and the housing. The commutation system typically employs a pair of precious metal brushes, which significantly reduce brush sparking. Lower brush sparking leads to reduced electromagnetic interference (EMI) and electromagnetic emissions.
Application Scenarios
Thanks to their fast response, low inertia, and high efficiency, coreless motors are widely used in the following applications:
Fast-response servo and tracking systems
Such as rapid flight direction adjustment in missiles, high-precision optical drive servo systems, fast autofocus mechanisms, highly sensitive recording and detection equipment, industrial robots, and bionic prosthetics. Coreless motors effectively meet the stringent requirements for high-speed response and precise control in these systems.
Applications requiring smooth and continuous operation
Including portable instruments, personal wearable devices, field operation equipment, and electric vehicles. Under the same power supply conditions, the use of coreless motors can significantly reduce energy consumption, often extending operating time by more than double.
Various aerial vehicles
Including aerospace systems, aviation platforms, and model aircraft. With their lightweight, compact size, and low energy consumption, coreless motors help minimize the overall weight of flying systems.
Consumer electronics and industrial products
When used as actuators, coreless motors can significantly enhance product performance and perceived quality.
Multi-functional applications
Due to their high energy conversion efficiency, coreless motors can also be used as generators. Their linear operating characteristics make them suitable for use as tachogenerators. When combined with a gearbox, they can also function as torque motors.
Limitations and Precautions
One limitation of coreless motors occurs under abnormal power supply conditions when the DC motor is at standstill. If one phase of the winding is disconnected or a single phase of the power supply is improperly energized, two rotating magnetic fields of equal magnitude and opposite direction may be generated. The resulting torques acting on the rotor cancel each other out, leading to zero starting torque and failure to start.
This condition can be potentially hazardous. Therefore, during operation and maintenance, it is essential to check:
Whether any winding phase is open-circuited
Whether the power supply circuit is interrupted or a fuse has blown
Whether there is current loss in any phase of the winding
2.3 Coreless motors feature reliable operational stability, high energy density, fast start-up and braking response, and reduced electromagnetic interference.
2.4 Compared with brushless coreless motors, brushed coreless motors feature longer service life, higher rotational speed, and the presence of iron losses.

Whether for frameless torque motors used in humanoid robots, joint motors, or coreless motors, Honest Automation has mature customer cases covering stator and rotor winding as well as motor assembly. We have already helped several robotics manufacturers achieve mass production.
If you are planning prototyping or large-scale production for humanoid robots, frameless torque motors, or coreless motors, feel free to leave us a message online to request case studies and customized manufacturing solutions.







