1. Introduction: Why High-Volume EV Motor Production Matters Today
As global electric vehicle adoption accelerates, electric motors have moved from being a core component to becoming a strategic differentiator. While early competition focused on motor performance indicators such as efficiency, power density, and torque output, the industry has now entered a new phase—manufacturing capability competition.

For leading EV motor manufacturers, the real challenge is no longer whether a motor can perform well in a prototype or test vehicle, but whether it can be produced at scale, with consistent quality, stable yield, and predictable cost. High-volume production capability has become a defining factor that separates industry leaders from followers.
2. What Defines a “Top” EV Motor Manufacturer?
When discussing top EV motor manufacturers, size or brand recognition alone is not sufficient. From a manufacturing and industrialization perspective, leadership is defined by the ability to consistently deliver high-quality motors at scale.
Key characteristics typically include:
Scalable production capacity across multiple plants or regions
High automation levels in stator and rotor manufacturing
Stable and repeatable processes rather than manual-dependent operations
Proven ability to transition from prototype to mass production
Long-term production planning aligned with vehicle platform roadmaps
In this sense, “top” EV motor manufacturers are not simply strong in R&D—they excel in industrial execution.
3. Common Manufacturing Challenges in High-Volume EV Motor Production
Even the most advanced EV motor manufacturers face significant challenges when scaling production. These challenges become more pronounced as output increases.
3.1 Consistency Across Large Production Batches
Maintaining uniform electromagnetic performance, mechanical accuracy, and electrical insulation quality across thousands—or millions—of motors requires extremely tight process control.
3.2 Increasing Complexity in Stator Manufacturing
The industry trend toward higher slot fill factors and improved efficiency has driven adoption of advanced winding technologies such as hairpin or segmented stators. While beneficial for performance, these technologies significantly increase manufacturing complexity.
3.3 Welding and Joining Reliability
Processes such as hairpin welding, terminal joining, and connection of star points demand high precision. Minor variations can lead to resistance imbalance, thermal issues, or long-term reliability risks.
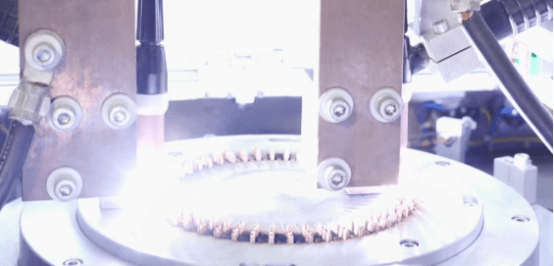
3.4 Quality Control at Scale
Traditional end-of-line inspection is no longer sufficient. High-volume production requires inline inspection, traceability, and early defect detection to prevent downstream quality losses.
3.5 Labor Dependency and Cost Pressure
Manual operations introduce variability and limit scalability, especially in regions facing rising labor costs or skilled workforce shortages.
4. Manufacturing Technologies Behind High-Volume EV Motor Production
High-volume EV motor production is enabled by a combination of advanced manufacturing technologies working together as a system.
4.1 Advanced Stator Winding Technologies
Technologies such as hairpin winding, concentrated winding, and precision needle or flyer winding allow higher slot fill factors and better electromagnetic performance, provided they are executed with high repeatability.
4.2 Automated Rotor Assembly Processes
Rotor assembly—including magnet insertion, bonding, and balancing—requires automation to ensure mechanical stability and long-term durability at scale.
4.3 Inline Inspection and Quality Monitoring
Vision systems, electrical testing, and dimensional measurement integrated directly into the production line allow manufacturers to detect deviations early and maintain process stability.
4.4 Digitalization and Production Data Traceability
Data-driven manufacturing enables real-time monitoring, root cause analysis, and continuous process optimization—essential for high-volume, multi-shift operations.
5. Production System Design: From Prototype to Mass Production
One of the most common misconceptions in EV motor manufacturing is assuming that a successful prototype can be easily scaled into mass production. In reality, prototype success does not guarantee production success.
Key considerations include:
Process window definition for stable mass production
Modular versus integrated line design, balancing flexibility and throughput
Early planning for automation, rather than retrofitting later
Alignment between product design and manufacturability
Leading manufacturers treat production system design as a parallel activity to motor design—not an afterthought.
6. Industry Patterns: How Leading EV Motor Manufacturers Build Scalable Production
While each company has its own strategy, certain patterns consistently appear among leading EV motor manufacturers:
Automation planning begins at the early design stage
Customized production solutions are preferred over generic, standard machines
Manufacturing systems are designed for future variants and capacity expansion
Close collaboration exists between R&D, manufacturing, and automation partners
These practices reduce scale-up risk and enable smoother transitions between product generations.
7. The Role of Specialized Motor Automation Partners
Behind every high-volume EV motor production system is a network of specialized partners. For leading manufacturers, automation partners are not simply equipment suppliers—they act as system enablers.
Their role typically includes:
Translating motor design requirements into manufacturable processes
Integrating multiple processes into a cohesive production line
Ensuring long-term stability, serviceability, and scalability
Supporting global deployment and localization needs
Experienced motor automation partners such as Honest Automation focus on complete stator and rotor production solutions, helping manufacturers bridge the gap between design intent and industrial reality.

8. How Automation Enables Consistency, Yield, and Scalability
Automation is not adopted solely to reduce labor costs. Its true value lies in process consistency and predictability.
Key benefits include:
Reduced human-induced variability
Stable and repeatable process windows
Higher and more predictable yield rates
Easier replication of production lines across multiple sites
For high-volume EV motor production, automation is not optional—it is foundational.
9. What Emerging EV Motor Manufacturers Can Learn from Industry Leaders
For companies aiming to scale their EV motor production, several lessons stand out:
Design motors with manufacturability in mind from the beginning
Invest early in production system planning
Avoid over-reliance on manual processes during scale-up
Choose manufacturing strategies that support long-term growth, not short-term output
Learning from established industry leaders can help emerging manufacturers avoid costly mistakes during industrialization.
10. High-Volume Production Is a System, Not a Single Machine
High-volume EV motor production is not achieved through individual machines or isolated processes. It is the result of well-designed, integrated manufacturing systems that balance performance, quality, and scalability.
As the EV market continues to evolve, manufacturers that invest in robust production systems—and work with experienced automation partners—will be best positioned to lead the next phase of electric mobility.






