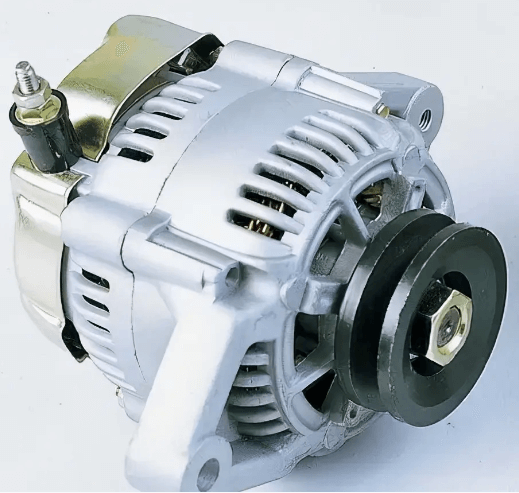
The automotive alternator is an important part of a vehicle’s electrical system, responsible for generating the necessary power to keep the battery charged and to run electrical accessories. Without a functioning alternator, the battery will quickly deplete, leading to problems such as dimmed headlights and a weak or dead battery.
Structure
An alternator generally consists of four parts: a rotor, a stator, a rectifier, and end covers.
A. Rotor
The function of the rotor is to generate a rotating magnetic field. It consists of claw poles, a magnetic yoke, magnetic field winding, a collector ring, a rotor shaft, and so on.
When DC current is supplied to the collector ring, current flows through the magnetic field winding and generates axial magnetic flux, causing one claw pole to be magnetized to the N pole and the other to the S pole, thus forming six pairs of interlaced magnetic poles. When the rotor rotates, a rotating magnetic field is formed.
B. Stator
The function of the stator is to generate alternating current. It consists of stator core and stator winding:
1. The stator core is made of silicon steel sheets with slots in the inner ring, where the stator winding wires are placed;
2. The stator winding has three phases, typically connected in star or delta configuration, to produce a three-phase alternating current. The winding is carefully designed to produce a three-phase electromotive force with equal frequency, amplitude, and a 120° phase difference.
C. Rectifier
The function of the rectifier is to convert the three-phase alternating current generated by the stator winding into direct current. It is usually composed of multiple silicon diodes to form a three-phase bridge full-wave rectifier circuit.
D. End Cover
The end cover is generally divided into two parts: the front end cover and the rear end cover, which play the role of fixing the rotor, stator, rectifier, and brush components.
The end covers are generally cast from aluminum alloy, which has good heat dissipation properties and can effectively prevent magnetic flux leakage.
Principle
The working principle of automobile alternators is generally based on the law of electromagnetic induction and the law of electromagnetic force. The general principle of its construction is: to use appropriate magnetic and electrically conductive materials to form magnetic circuits and circuits that conduct electromagnetic induction with each other to generate electromagnetic power and achieve the purpose of energy conversion.
After the engine is started and ignited, the generator speed gradually increases. When its output voltage is equal to the battery voltage, the car's power supply state changes to the generator to provide energy for the car's operation, and the indicator light goes out.
The external circuit energizes the excitation winding through the brush, generating a magnetic field in the rotor winding. Under the action of the magnetic field force, the rotor rotates and generates a rotating magnetic field in the stator winding; the magnetic flux changes alternately in the stator winding, and the stator acts on the rotating magnetic field. It induces and outputs AC electromotive force. The AC power is converted into DC power under the action of the rectifier, and then normal power generation can be generated. Provide energy to other devices and charge batteries.
Classification
Automotive alternators can be mainly divided into the following types according to their different structures and working principles:
A. Ordinary alternator
Working Principle: The rotating magnetic field of the rotor induces AC electromotive force in the stator winding, which is rectified by the silicon rectifier diode and outputs DC power.
Advantages: simple structure, low cost, and broad application;
Disadvantages: A voltage regulator is required to stabilize the output voltage, and there are brushes and slip rings, making maintenance difficult.
B Claw poles Brushless Alternator
The field winding of a claw-pole brushless alternator is stationary and is fixed to the rear end cap via a yoke bracket, so no brushes are required.
Working principle: Only one of the two claw poles is directly fixed on the motor rotor shaft, and the other claw pole is fixed on the previous claw pole with a non-magnetic connecting ring. When the rotor rotates, one claw pole drives the other claw pole to rotate together in the stator. When DC current passes through the magnetic field winding, the claw pole is magnetized, forming a rotating magnetic field.
Advantages:
1. Simple structure, easy maintenance, and reliable operation;
2. The brushes and collector rings are eliminated, reducing the risk of unstable power generation and failure.
Disadvantages:
1. The connection process between claw poles is relatively complex;
2. Due to the increase in the gap in the magnetic circuit, the excitation current of the generator needs to be increased under the same output power. Therefore, the increase in the gap in the magnetic circuit requires a more sophisticated design to ensure the magnetic field strength and generator efficiency.

C. Permanent Magnet Brushless Alternator
Working principle: The permanent magnet is used as the rotor pole to generate a rotating magnetic field, eliminating the need for excitation windings and brushes, and simplifying the structure. Commonly used permanent magnet materials for the rotor include ferrite, chromium-nickel cobalt, rare earth cobalt, neodymium iron boron, etc.
Advantages:
1. It’s compact, lightweight, simple structure, easy maintenance and long service life;
2. Due to the large transmission ratio, that is, the engine speed is low and the generator speed is high, the charging performance of the generator is good at low engine speeds;
3. High power output can save metal materials;
4. No excitation loss, efficiency can be increased by more than 10%;
5. In the voltage controller, since only about 10mA current of the control pole passes through the contacts, contact wear can be reduced, and the voltage adjustment structure is simple;
6. Since the magnetic permeability of the permanent magnet is close to the magnetic permeability of the air, the armature reaction magnetic resistance increases, so the non-sinusoidal distortion of the induced electric potential is reduced.
Disadvantages:
1. Temperature sensitivity: Permanent magnet materials may be sensitive to temperature changes, and high temperatures may cause their magnetic force to decrease;
2. Complex recycling and processing: The recycling and processing of permanent magnet materials after the generator is scrapped is relatively complex and may have an impact on the environment.
D. Automobile Double Rectifier Generator
Working principle: Based on the traditional three-phase stator winding, the number of winding turns is increased and the terminals are led out, and it is equipped with two sets of three-phase bridge rectifiers. At low speeds, the original winding and the additional winding are connected in series to increase the output voltage; at high speeds, only the original winding works, ensuring power output at high speeds.
Advantages:
1. It reduces the charging speed of the generator, while ensuring high-speed and large current output, increasing the effective power of the generator;
2. Simple structure, reliable operation, and performance improvement can be achieved by increasing the number of winding turns and rectifiers.
Disadvantages:
1. Compared with standard generators, its system complexity increases. Double rectifier generators require additional windings and rectifiers, which increases the complexity of the system;
2. The added windings may slightly increase the weight of the generator, which will have a certain impact on the overall weight distribution of the vehicle.
Functions
1. Power supply: When the car is driving, the alternator provides power to the vehicle's electrical system, including the starter motor, lighting system, ignition system, on-board electronic equipment, and so on.;
2. Charging: The generator is also responsible for charging the battery to ensure that the battery is always fully charged and provides sufficient power for starting the car and other devices that require larger currents;
3. Voltage regulation: Through the built-in or external voltage regulator, the alternator can automatically adjust the output voltage to maintain voltage stability and avoid damage to the electrical system due to too high or too low voltage;
4. Energy conversion: Convert the mechanical energy of the engine into electrical energy. The engine drives the generator rotor to rotate through the belt, thereby generating electric current;
5. Improve fuel efficiency: In some cases, the generator can reduce the load on the engine. Especially when the vehicle is traveling at high speed, the engine can provide sufficient power and reduce the engine's demand for electricity, thus improving fuel efficiency;
6. Maintain the health of the vehicle's electrical system: Maintain the health of the vehicle's electrical system through continuous power supply and charging to avoid system failures caused by insufficient power.
It can be seen from the above that the importance of the alternator in the automotive electrical system ensures the normal operation of the automotive electrical equipment and the optimization of the overall vehicle performance.
HONEST Automation has been engaged in motor equipment manufacturing for 18 years as well as a provider of BSG motor stator assembly line solutions. We have served lots of well-known automobile manufacturers and automotive parts suppliers from all over the world.
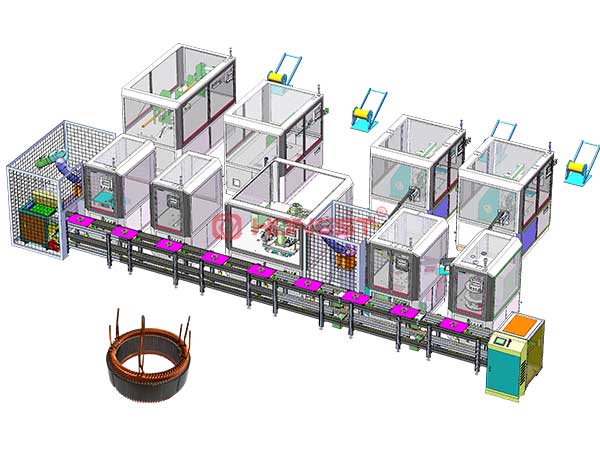
The picture shows HONEST Automation automotive hairpin motor stator assembly line, which is suitable to be used in the automotive generator field.
If you need any solutions for electrical equipment or have any inquiries regarding our motor equipment offerings, please feel free to contact Shenzhen HONEST and we look forward to receiving your message.






