1. Categories of Brushless Motors
A brushless motor is an advanced type of electric motor that uses electronic commutation and is characterized by high efficiency, low noise, long life, and high energy density
The classification of brushless motors can be based on different features and application requirements, which can be divided into the following categories:
(1) Sensor Presence
Sensored Brushless Motor: It utilizes hall sensors, rotary encoders, and so on, to detect the rotor’s position for precise control;
Sensorless Brushless Motor: It does not use external sensors and relies on motor control algorithms to estimate the rotor’s position and speed.
(2) Rotor Type
Internal Rotor Brushless Motor: The rotor is located inside the motor, typically with a smaller volume, and suitable for applications requiring higher rotational speeds;
External Rotor Brushless Motor: The rotor is located outside the motor, typically with a larger volume, and it can be able to provide greater torque, suitable for applications requiring larger power output.
(3) Magnet Installation Method
Surface Permanent Magnet (SPM): The magnets are installed on the outer surface of the rotor.
Interior Permanent Magnet (IPM): The magnets are embedded within the rotor, which helps to improve the motor’s efficiency and torque density.
(4) Winding Method
Concentrated Winding: The Winding is concentrated in specific slots of the motor, commonly used in high-performance motors.
Distributed Winding: The winding is distributed across multiple slots of the motor, which helps to produce a smoother torque.
(5) Motor Structure
Radial Flux Motor: The magnetic field is perpendicular to the motor’s axis.
Axial Flux Motor: The magnetic field is parallel to the motor’s axis.
(6) Control Method
Square Wave Drive: It is controlled by using square wave signals, suitable for simple on or off control.
Sinusoidal Wave Drive: It is controlled by using sinusoidal wave signals, suitable for applications that require smoother operation and higher precision control.
(7) Application Fields
Industrial Brushless Motors: They are designed for industrial automation and mechanical drives.
Automotive Brushless Motors: They are used for driving and auxiliary systems in electric vehicles and hybrid vehicles.
Aerospace Brushless Motors: They are used in propulsion and control systems for aircraft, drones, and other aerospace vehicles.
This article will focus on the introduction of internal rotor brushless motors and external rotor brushless motors.
2. Internal Rotor Brushless Motor -The rotor rotates with the motor’s main shaft, while the motor housing is stationary.
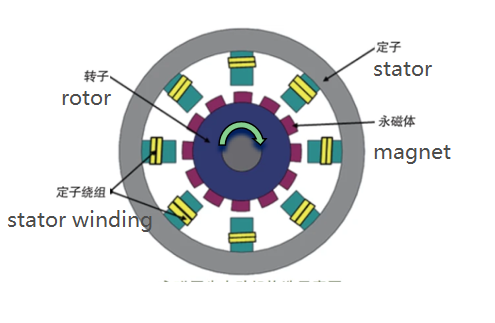
A. Feature
The rotor of an internal rotor brushless motor is located at the center of the motor, surrounded by the stator. The design allows the motor to maintain performance while achieving a more compact volume. Internal rotor motors typically also use high-performance permanent magnet materials to achieve greater magnetic flux density and smaller rotational inertia. In addition, the winding of the internal rotor motor is located on the outside of the rotor, which helps improve the motor’s heat dissipation efficiency.
B. Advantages
Miniaturization: With the rotor located at the center of the motor, internal rotor brushless motors have a more compact volume, making them easy to integrate into various devices and suitable for applications with limited space.
High Speed: The smaller moment of inertia allows internal rotor brushless motors to achieve higher speeds, suitable for applications requiring rapid rotation.
Fast Response: The internal rotor design facilitates the motor’s quick start and stop, suitable for situations that demand fast dynamic response, such as precision positioning systems.
Heat Dissipation: With winding located on the outside of the rotor, it helps to improve heat dissipation efficiency, thereby enhancing the motor’s continuous working capacity and lifespan.
C. Application Fields
Household Appliances: Such as variable frequency drives for air conditioners and washing machines, providing efficient and low-noise operation.
Medical Equipment: Some precision medical devices, such as small blood pumps in artificial hearts, surgical tools, and so on, provide precise control.
Precision Industry: It is also used in numerical control machines, robots, and other situations requiring high-precision control, ensuring processing accuracy and efficiency.
Automotive: It is used for electric windows, windshield wipers, electric seats, and so on, providing a power source with high efficiency and a long lifespan.
3. External Rotor Brushless Motor - The rotor rotates with the motor housing, while the motor’s main shaft is stationary.
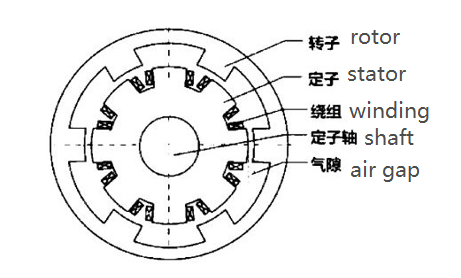
A. Features
The rotor of an external rotor brushless motor is located on the outside of the motor, while the stator is located in the center. The design, with the rotor on the outside of the motor, allows the motor to provide greater torque, suitable for applications with high torque requirements. The permanent magnets of the external rotor motor are attached to the housing, which serves as the rotor and is connected to the output shaft. When the motor operates, the rotation of the brushless external rotor motor housing drives the output shaft. Because the mass of the rotor is concentrated on the housing, the rotational inertia of the external rotor motor is greater than that of the internal rotor motor.
B. Advantages
High Torque: The external rotor design helps the motor to produce a large starting torque to power-to-weight ratio, suitable for situations requiring high torque.
Stability: During constant-speed rotation, the external rotor brushless motor can provide a stable speed, suitable for applications with high requirements for speed stability.
Simple Structure: The structure of the external rotor motor is relatively simple, facilitating maintenance and manufacturing, and reducing production and maintenance costs.
C. Application Fields
Industrial Applications: Such as fans, pumps, and other equipment requiring high torque, providing efficient and stable power.
Fitness Equipment: The power source for sports equipment like treadmills and bicycles, providing a smooth and reliable exercise experience.
Electric Vehicles: The driving motor for electric bicycles, electric scooters, and so on, providing high efficiency and good acceleration performance.
4. Differences Between Internal Rotor Brushless Motors and External Rotor Brushless Motors:
A. Principle Differences
Internal Rotor: The rotor in an induction motor, composed of a rotating shaft core and closed conductors embedded in the core, is driven by the rotating magnetic field generated by the stator winding to produce high-speed rotational motion. The rotor ends are fitted with rolling bearings and are installed and fixed within the motor housing end covers.
External Rotor: Maintains magnetic balance at the center of the motor. However, in the case of force instability, any slight displacement can cause the rotor to deviate from its original position, and it may even completely lose contact with the stator. Radial position suspension control is used to eliminate eccentric displacement of the motor rotor.
B. Structural and Design Comparison
The design of the internal rotor brushless motor is more compact, and suitable for miniaturization and high-speed applications, while the external rotor brushless motor, due to its larger size and structural simplicity, is more suitable for applications requiring high torque.
C. Performance and Efficiency Comparison
Internal rotor brushless motors have advantages in high-speed operation and rapid response, while external rotor brushless motors have advantages in providing high torque and stability.
D. Application Scenario Selection
Internal rotor brushless motors are more suitable for situations with strict requirements for space and speed, while external rotor brushless motors are more suitable for applications with high torque requirements.
E. Heat Dissipation Performance
The internal rotor motor can improve heat dissipation efficiency by adding heat dissipation fins or fans on the outside of the stator to increase airflow.
The heat dissipation design of the external rotor motor may be limited by space, as the rotor is located on the outermost layer of the motor, making the installation of heat dissipation fins or fans less convenient than for internal rotor motors.
F. Cost-Benefit Analysis
Internal rotor brushless motors may have higher costs due to high-performance magnets and complex manufacturing processes. Although the initial investment for external rotor brushless motors is higher, their high efficiency and long lifespan result in lower long-term operating costs.
Both internal and external rotor brushless motors have their advantages and can be selected based on actual application requirements.
5. About HONEST Automation
HONEST Automation has been engaged in fully automatic rotor assembly line manufacturing for 18 years as well as a provider of motor equipment solutions. We have served plenty of well-known automobile manufacturers and automotive parts suppliers from all over the world.

If you need any solutions for brushless motor equipment or fully automatic rotor assembly line, please feel free to contact HONEST Automation and we sincerely look forward to receiving your message.






