Due to the insufficient power of the original 12V automotive battery to meet the demands of mild hybrid systems, automakers introduced a 48V power system to enable more efficient mild hybrid technology.
The original 12V system primarily powers the in-vehicle infotainment and lighting systems, while the 48V system is dedicated to driving the air conditioning compressor, enabling energy recovery, and assisting the engine to improve overall system efficiency. This dual-voltage system working in synergy not only significantly enhances fuel economy but also reduces tailpipe emissions, making a positive impact on the environment.
With ongoing technological advancements, the original dual-voltage architecture of 12V + 48V has evolved into a single 48V system. Today, we will focus on introducing the two mainstream configurations of the 48V system.
The 48V mild hybrid system is mainly composed of three core components: the electric motor, the power battery pack (primarily lithium-ion), and the voltage controller (DC-DC converter). Among these, the motor type plays a particularly critical role and is generally categorized into two types: BSG (Belt Starter Generator) motors and ISG (Integrated Starter Generator) motors.
BSG Motor
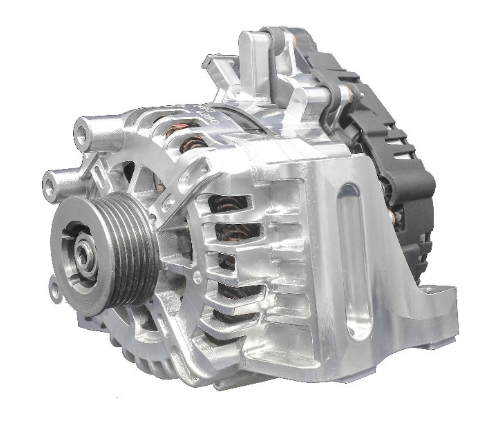
The BSG (Belt Starter Generator) motor is a belt-driven motor that connects to the engine via a belt system. In a conventional internal combustion engine, the front end typically includes an alternator connected to the crankshaft through a flexible belt. When the engine is running, a small portion of its energy is transmitted to the alternator for electricity generation. In a mild hybrid architecture, the BSG motor replaces this traditional alternator and is often referred to as a P0 motor.
During normal engine operation, the BSG motor does not provide propulsion assistance but functions solely as a generator, continuously charging the battery. However, when the vehicle is at a stop and begins to move again, the BSG motor engages. It uses the belt drive to rapidly spin up the engine to a more efficient RPM range, enabling quick engine restarts and providing auxiliary torque to support the engine during acceleration.
Since the BSG motor transfers power to the wheels in a series configuration via the engine, it cannot independently drive the vehicle and therefore does not support pure electric driving. It is typically used in micro-hybrid (12V–25V) and mild hybrid (48V) systems. Due to its limitations, BSG motors are generally paired with smaller displacement engines, such as the 1.5T engine in certain Buick models or earlier Mercedes-Benz C-Class models.
ISG Motor
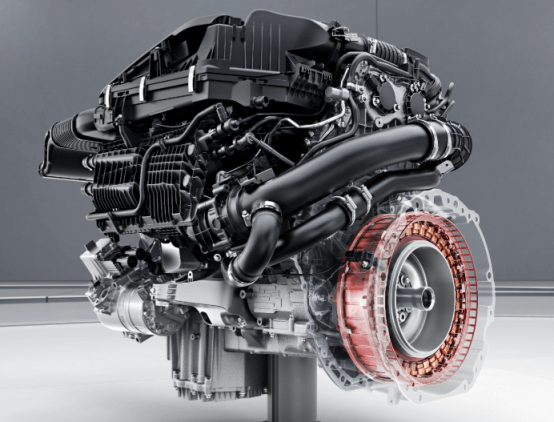
Another approach is the use of an ISG (Integrated Starter Generator) motor, also known as a P1 motor. This motor is mounted at the end of the engine crankshaft, positioned between the engine and the transmission. In this configuration, the crankshaft itself functions as the rotor of the electric motor.
Compared to the belt-driven BSG motor, the ISG layout reduces the mechanical load on the engine and significantly improves overall system efficiency. During acceleration, the ISG motor can directly provide torque assistance; during deceleration, it enables regenerative braking and energy recovery. In essence, the system evolves from the BSG's series configuration into a more versatile and efficient parallel structure, supporting multiple hybrid operating modes.
As hybrid powertrain technologies continue to evolve, the advantages of 48V mild hybrid systems are gradually diminishing. Whether utilizing a BSG or ISG motor, these systems are fundamentally categorized as mild hybrids, where the electric motor is primarily used for energy recuperation and providing limited power assistance under specific conditions. However, it cannot drive the vehicle independently, which makes its impact on fuel consumption relatively modest.
Today, many plug-in hybrid (PHEV) and full hybrid models incorporate P0 or P1 motors as auxiliary components within more advanced hybrid architectures. For example, Honda and Toyota use P1+P3 configurations in their hybrid systems, while BYD’s DM 3.0 platform offers combinations such as P0+P3, P0+P4, and even P0+P3+P4.
Although standalone 48V mild hybrid systems using BSG or ISG motors can offer some improvements in fuel efficiency, they still fall under the category of low-level hybridization with limited performance gains. With the rise of more sophisticated hybrid solutions, 48V mild hybrid technology is losing its edge and is no longer regarded as a cutting-edge solution.
HONEST Automation offers reliable and well-established assembly lines for 48V BSG motor stators and ISG motors, with customizable solutions tailored to your production needs. Feel free to contact us for personalized proposals and pricing. Our technical experts are here to provide you with professional guidance and full support throughout the process.





