Wheel Side Motor
The Wheel Side Motor, also known as a wheel-side drive system, is a driving method in which the electric motor is installed on the wheel of the vehicle, but unlike the hub motor, the wheel-side motor is not directly integrated into the wheel. The wheel-side motor usually transmits power to the wheels via a short shaft or other mechanical connection, still maintaining some mechanical separation.

The advantages of wheel-side motors:
A. Reduce the mechanical complexity of the vehicle because it simplifies the power transmission path and does not require traditional differentials, drive shafts, and other components;
B. Provide independent wheel-side drive, which contributes to the vehicle’s drive efficiency and handling;
C. Improves the efficiency of energy recovery as the motor is closer to the wheel;
D. It can achieve independent wheel speed control, helping to realize advanced driver assistance systems and automatic driving functions.
The disadvantages of wheel-side motors:
A. Higher unsprung mass than conventional center drive motor systems, although generally less than hub motors;
B. Heat dissipation can be a challenge because the motor is still external to the vehicle chassis;
C. Maintenance and replacement may be more difficult than center drive motors because the motor is located closer to the wheels;
D. Additional space may be required to install the wheel-side motors, which may affect the vehicle’s design and interior space.
Hub Motor
The Hub Motor, also known as in-wheel motor or direct drive motor, is an electric motor installed in the hub of a vehicle. It is mainly used in electric vehicles, such as electric bicycles, electric motorcycles, electric cars, and some electric wheelchairs. Hub motors are designed so that the motor is integrated directly into the wheel and can power the wheel without needing traditional power transmission systems such as gearboxes, driveshafts, or differentials.

The future development trends of hub motors mainly include:
A. Cost reduction: with the advancement of technology, the cost of hub motor will gradually decline, making it more suitable for low-end and mid-range electric vehicles;
B. Improvement of heat dissipation efficiency: by improving the motor structure and heat dissipation system, the heat dissipation efficiency of hub motors will be improved, thus increasing the service life of the motors;
C. Performance improvement: with the advancement of motor technology, the performance of hub motors will be improved to meet higher-demand application scenarios.
The market forecast for the hub motor:
Recently, the demand for hub motors has grown dramatically due to increased production and industrial interest in electric vehicles and the many benefits of electric vehicles. According to relevant research reports, the global hub motor market is expected to reach 2.8 billion dollars in 2024, a year-on-year increase of 25%, of which China, the United States, and Europe will be the main growth drivers of the global hub motor market.
China Market
China is the world’s largest in-wheel motor market, and the market size is expected to reach 1.5 billion in 2024, a year-on-year increase of 28%. The Chinese government vigorously promotes the development of new energy vehicles, which is the main driving force for the growth of the in-wheel motor market. In addition, the technological level of Chinese hub motor companies continues to improve, and product competitiveness continues to increase, which also provides support for market growth.
US Market
The United States is the second largest hub motor market in the world, with the market size expected to reach 800 million dollars in 2024, a year-on-year increase of 22%. The U.S. government has also introduced a number of policies to support the development of new energy vehicles, which will provide a good policy environment for the hub motor market. In addition, the growing demand for high-performance hub motors in the U.S. market is also providing impetus for market growth.
European Market
Europe is the third largest hub motor market in the world. The market size is expected to reach 500 million dollars in 2024, with a year-on-year growth of 20%. The European government’s increasing support for new energy vehicles will provide a broad market space for the hub motor market. In addition, the European market has high safety and reliability requirements for hub motors, which will promote hub motor enterprises to continuously improve product technology and quality.
What’s more, the hub motor market in Asian countries and regions such as Japan and South Korea will also maintain its growth momentum.
The global hub motor market will generally maintain the growth trend in 2024. With the popularity of new energy vehicles, hub motors will usher in a broader space for development.
The Hub Motor vs. the Wheel-side Motor
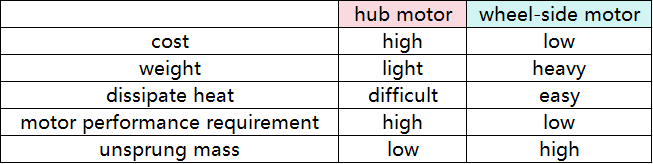
The main function of hub motors and wheel-side motors is to provide power and control to the wheels in electric vehicles. The wheels of the vehicle are driven between them, instead of driving the wheels through a series of mechanical transmission systems such as internal combustion engines, gearboxes, drive shafts, and differentials in traditional internal combustion engine vehicles.
The following are the differences between hub motors and wheel-side motors:
A. Mounting location: hub motors are integrated directly into the hub of the wheel, replacing the traditional wheel center; wheel-side motors are mounted near the wheel, not in the hub, and they transmit power via a short shaft or other means;
B. Unsuspended mass: hub motors increase the unsuspended mass of the wheel, which may affect the performance and comfort of the suspension system; compared with hub motors, wheel-side motors have less unsuspended mass, which helps maintain better driving quality;
C. Structural design: hub motors have a more compact structure because they do not require traditional power transmission components such as transmission shafts and differentials; wheel-side motors simplify the traditional power transmission path, but still require some connectors;
D. Heat dissipation issue: due to the limitation of location, hub motors have difficulty in heat dissipation; wheel-side motors have more heat dissipation methods and space than hub motors;
E. Maintenance and replacement: hub motors can be more complicated to maintain and replace due to their close integration with the wheel; wheel-side motors are also more difficult to maintain and replace, but are also usually easier to maintain than hub motors;
F. Energy recovery: hub motors are more efficient in energy recovery during braking because they are directly connected to the wheels; wheel-side motors are slightly inferior to hub motors;
G. Applicability: hub motors are commonly used in e-bikes, e-scooters, and some small electric vehicles; wheel-side motors are suitable for vehicles that need to control each wheel independently to improve handling, such as some electric cars and commercial vehicles.
Both hub motors and wheel-side motors have their advantages and limitations, so the selection needs to be weighed based on specific application scenarios and design requirements. The hub motors are widely used in small electric vehicles due to their simple design and small space requirements. However, the wheel-side motors are used in certain larger electric vehicles because they provide independent drive and high-performance control with relatively little impact on ride quality. As electric vehicle technology advances, the performance and cost-effectiveness of both types of motors continue to improve.
If you are interested in hub motor winding machine, please contact us at your times.