With the rapid evolution of vehicle electrification and intelligent systems, the number and complexity of electric motors used in modern automobiles continue to increase. From high-power traction motors in electric vehicles to precision auxiliary motors in conventional cars, each motor type presents distinct structural characteristics and manufacturing challenges.
Below is an in-depth overview of major automotive motor types and the key difficulties involved in their manufacturing.
1. Hairpin Drive Motors (New Energy Vehicle Traction Motors)
Hairpin motors are widely used in electric vehicles (EVs) due to their high slot fill factor, superior power density, and excellent thermal performance. Unlike traditional random-wound stators, hairpin stators use rectangular copper conductors that are pre-formed, inserted into stator slots, twisted, and then welded—typically via laser welding.
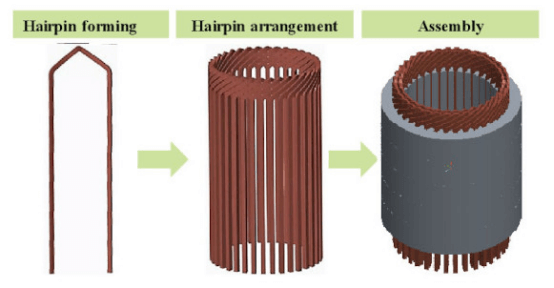
However, manufacturing hairpin motors presents significant technical challenges:
Precise forming and insertion of rectangular copper wires
Accurate twisting and positioning of hairpins
High-precision laser welding with minimal spatter and stable penetration
Strict control of insulation integrity and phase-to-phase isolation
High consistency requirements for mass production
Manual assembly is virtually impossible due to the required welding precision, dimensional consistency, and electrical reliability. Fully automated stator production lines are essential to ensure stable quality, high efficiency, and scalable output.
2. BSG Motors (Belt Starter Generator)
BSG (Belt Starter Generator) motors are core components in mild hybrid vehicles (48V systems). They integrate starting and power generation functions, requiring high torque density and fast dynamic response.

Manufacturing challenges include:
High slot fill winding under compact stator designs
Tight concentricity requirements between the rotor and stator
Strict NVH (Noise, Vibration, Harshness) control
High reliability under frequent start-stop cycles
Because BSG motors operate under continuous mechanical load and dynamic switching conditions, manual winding and assembly cannot guarantee sufficient performance consistency. Automated winding and assembly solutions are critical to achieving reliable large-scale production.
3. Oil Pump Motors
Oil pump motors are typically used in transmission systems or engine lubrication systems. These motors operate in high-temperature and oil-immersed environments, requiring exceptional durability and sealing performance.
Manufacturing difficulties include:
High-precision stator winding for stable torque output
Rotor dynamic balance control
Seal integrity and contamination prevention
Consistency under high-volume production
Manual assembly increases variability and contamination risk, which directly affects motor lifespan and performance. Automated stator winding and rotor assembly significantly improve production stability and yield rate.
4. Brake Motors (e.g., EPB Motors)
Brake motors, such as those used in Electronic Parking Brake (EPB) systems, demand extremely high reliability and precise torque control. Safety-critical applications leave no room for inconsistency.
Manufacturing challenges:
High-precision micro-motor winding
Stable commutation or electronic control integration
Strict torque testing and end-of-line inspection
Zero-defect quality control requirements
Given the safety-critical nature of braking systems, manual assembly cannot ensure the required process traceability and consistency. Automated production lines with integrated testing systems are essential.
5. EPS Motors (Electric Power Steering Motors)
EPS motors are among the most demanding automotive motors in terms of torque response, control precision, and durability. They must provide stable steering assistance under various driving conditions.
Manufacturing challenges include:
High-density stator winding
Rotor magnet insertion accuracy
Strict air-gap control
Comprehensive NVH management
100% performance testing requirements
Due to tight tolerances and safety-critical application, EPS motor production requires advanced automated winding, rotor assembly, and intelligent testing systems to ensure consistent quality.
6. Water Pump Motors
Electric water pump motors are increasingly used in EV thermal management systems and engine cooling systems. These motors require high efficiency and long operational life.
Production challenges:
High-speed rotor balance control
Insulation reliability under high temperature
Compact structural assembly
High-volume production stability
Automated assembly solutions help ensure efficiency, reduce human error, and improve long-term reliability.
7. Cooling Fan Motors
Cooling fan motors are used in engine cooling modules and battery cooling systems. They operate continuously under variable speed conditions.
Manufacturing challenges:
Stable winding tension control
Rotor balance accuracy
Noise reduction requirements
Mass production consistency
Manual processes struggle to maintain winding uniformity and dynamic balance consistency, making automation essential.
8. Window Regulator Motors
Window regulator motors are widely used in passenger vehicles and require compact design and cost efficiency.
Production difficulties include:
Small stator winding precision
Gearbox assembly accuracy
Long lifecycle durability
High-volume cost control
Automated, semi-automatic or fully automatic assembly lines help improve production efficiency while maintaining consistent product quality.
9. Blower Motors
Blower motors are critical components in HVAC systems. They must operate quietly and efficiently over long durations.

Manufacturing challenges:
High-speed winding precision
Rotor balancing
NVH optimization
Stable mass production performance
Manual assembly cannot guarantee uniform electrical parameters and dynamic balance across large volumes, making automated production systems essential.
Manufacturing Challenges: Why Automation Is Essential
Across all automotive motor types, several common manufacturing challenges emerge:
Increasing winding complexity and higher slot fill requirements
Precision welding demands (especially for hairpin technology)
Strict consistency and traceability standards
Rising labor costs and workforce instability
High-volume production demands with zero-defect expectations
Manual assembly is no longer capable of meeting modern automotive industry standards for performance, safety, and scalability. Automated winding and assembly solutions are becoming the industry norm.
Honest Automation: One-Stop Solutions for Automotive Motor Manufacturing
Honest Automation specializes in providing customized solutions for automotive motor stator and rotor winding and assembly.
We provide:
Prototype development and motor sampling
Small-batch pilot production lines
Large-scale mass production lines
Our solutions include:
Standalone machines
Semi-automatic assembly systems
Fully automatic intelligent production lines
Multiple automotive customers and real production cases have validated our equipment technology. We have independently developed proprietary control systems that make equipment commissioning, parameter adjustment, and daily operation more efficient and user-friendly.
From hairpin motor to auxiliary automotive motors, Honest Automation delivers reliable, scalable, and high-performance manufacturing solutions tailored to customer requirements.
We welcome global motor manufacturers and automotive OEM suppliers to discuss customized solutions or visit our facility for technical exchange.






